
Preventive Care in Nursing and Midwifery Journal

Volume 15, Issue 3 (7-2025)
Prev Care Nurs Midwifery J 2025, 15(3): 24-40 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: IR.IAU.BABOL.REC.1402.115
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Rahmani N. Explaining the concept of moral distress in pediatric nurses: A hybrid concept analysis. Prev Care Nurs Midwifery J 2025; 15 (3) :24-40
URL: http://nmcjournal.zums.ac.ir/article-1-979-en.html
URL: http://nmcjournal.zums.ac.ir/article-1-979-en.html
Department of Nursing and Midwifery, Bab.C., Islamic Azad University, Babol, Iran. , na57ra@yahoo.com
Full-Text [PDF 810 kb]
(133 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (447 Views)
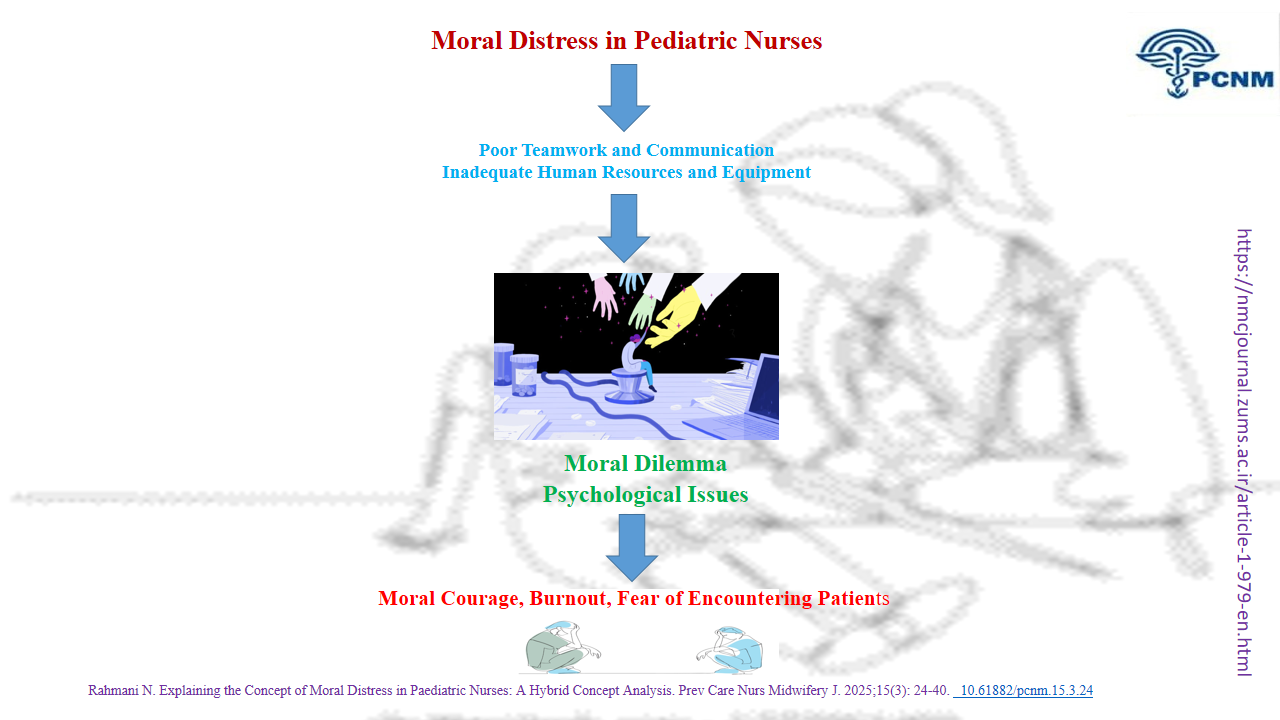
Table 1. Key Evidence on Moral Distress (2014-2024)
Table 2. Summary of Concept Analysis Findings: Themes and Categories from the Theoretical and Fieldwork Phases
The sample size was determined based on data saturation. Data collection continued until a point was reached where further data collection resulted in repeating previous data with no new information emerging. Sampling continued until data saturation was reached, which was defined as conducting three consecutive interviews without extracting new codes or thematic insights. Semi-structured individual interviews were used as the primary method of data collection. Data collection began with participants filling out consent forms. The interviews commenced with open-ended questions such as, “Please describe your experiences during a shift in the pediatric ward. What ethical issues did you encounter while caring for a child? What factors during child care caused your moral distress?” Then, clarifying questions were used based on participants’ responses and the research goals. Examples of these questions were “What contributed to your moral distress?”, “What happened next?”, “Can you please explain more?” “What do you mean by this?”. The author conducted the interviews after introducing himself and the objectives of the study. Interviews were conducted at the request of the participants at the workplace. Data collection continued until the development of categories and data saturation. The length of the interviews was 32 minutes, on average. All interviews were held in a quiet room in the participants’ workplace and were recorded with their consent (Table 4).

Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Pediatric nurse managers, hospital ethics committee members, and nursing educators specializing in pediatrics or ethics
Audience: Pediatric nurse managers, hospital ethics committee members, and nursing educators specializing in pediatrics or ethics
A refined understanding of moral distress specific to pediatric nursing, encompassing unique conflicts in child advocacy, family dynamics, and perceived powerlessness, provides a necessary foundation for effective intervention. Healthcare institutions should develop targeted support systems, such as structured ethics debriefings and pediatric-focused moral resilience training, informed by this nuanced conceptualization to mitigate distress and retain skilled nursing staff in challenging care environments.
Full-Text: (42 Views)
Introduction
Ethics is an inseparable part of human life and a branch of applied philosophy that studies behaviors and ideal ways of life, seeking to discern what is right or wrong and to explain good and bad behaviors in specific situations [1]. The concept of moral distress, first introduced by Andrew Jameton in 1984 as painful psychological disequilibrium, has been discussed for over three decades [2]. Generally, moral distress can be defined as emotional and mental discomfort experienced when an individual, despite having the awareness and ability for moral judgment, commits a moral infraction due to actual or perceived limitations [3].
Moral distress, derived from nursing ethics, is defined as psychological distress arising when individuals are restricted from acting upon what they know is right [4]. Ethical challenges in nursing can manifest internationally in at least two forms: ethical dilemmas and moral distress [5]. Nursing, due to its nature, is a profession that encounters numerous ethical issues. Studies have demonstrated that experiencing moral distress causes harm to the individual and their affiliated organization [6]. Research indicates that moral distress leads to challenges for healthcare workers, including nurses [7-9]. Since pediatric nurses interact directly with patients and their parents, providing care requires nurses with appropriate ethical and scientific competencies [10]. Moral distress is a phenomenon discussed in nursing literature and in the pediatric context, but it is often considered absent from discussions in clinical practice. It is caused by disproportionate care associated with overtreatment. Nurses can present a variety of symptoms, characterizing moral distress as a highly subjective experience. The pediatric contexts of practice should promote a healthy, ethical climate and work towards a moral community built with peer support, education, communication, leadership, and management involvement [4]. Fachini and colleagues, in a study on pediatric intensive care nurses, identified a lack of technological resources and inhumane care as sources of low-quality care and moral distress. Interestingly, moral distress can similarly arise from inequitable resource distribution at local and global levels [11]. Nurses have identified painful clinical procedures, parents withholding the truth from children, poor team performance, lack of human resources, and insufficient time to address the needs of children and families as causes of moral distress [12].
Studies clearly highlight the devastating consequences of moral distress, such as burnout among nurses. Burnout is defined as emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion resulting from professional activities, leading to avoidance and depersonalization [4]. This can result in lower-quality care, job transfers, or even nurses leaving the profession altogether [4, 12].
To navigate the complexities of healthcare in pediatric wards and mitigate the damages caused by moral distress, pediatric nurses must recognize and address the moral distress in themselves and others. Studying and understanding this issue enhances the professional ethical values of nurses and provides them with the courage to advocate for the best interests of the child and family, independent of others’ opinions [13]. Therefore, studying moral distress among pediatric nurses reflects progress toward more humane and realistic care for children [4]. Although various studies have identified the severe consequences of moral distress for nurses [14] few have examined moral distress specifically among pediatric nurses. This highlights the need to organize the existing evidence on this concept within this community and a particular setting [4].
A review of previous studies shows that concept analysis of moral distress has been conducted in nursing specialties such as neuroscience nursing [5], critical care nursing [15], and midwifery [16]. Despite significant research on moral distress, no review on moral distress in nurses working in paediatric settings has been identified, which reinforces the need to map and organise the available evidence on this concept in this specific population and context. Additionally, Jameton alerts that it is still necessary to develop knowledge around this subject for its incoherencies [4]. Moral distress is still an ambiguous concept and inadequately supported by existing knowledge, necessitating the development of further understanding due to its inconsistencies [4, 17]. In this regard, the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACCN) recognizes moral distress as a complex and challenging concept, with the greatest difficulty lying in identifying this phenomenon [4]. Due to the lack of clarity regarding the various characteristics of moral distress across different settings, reflecting the fluid and context-dependent nature of this concept [6]. Given the lack of an appropriate empirical definition of the concept of "moral distress" among Iranian nurses working in pediatric wards, it is very important to understand the diverse perspectives of these nurses and clarify this concept.
Objective
This concept analysis aims to explore how nurses experience moral distress and identify its variations. Thus, the primary objective of this study is to present evidence on the concept of moral distress, its causes, symptoms, characteristics, consequences, and the strategies proposed by pediatric nurses, using a hybrid Schwartz-Barcott and Kim approach.
Methods
This research employed a hybrid concept analysis model based on Schwartz-Barcott and Kim’s approach. In this research, the concept of moral distress among pediatric nurses was analyzed using a hybrid model. It was chosen because the desired approach extracts the concept of knowledge in clinical practice, and the concept under study has a clinical aspect. The hybrid model is based on concept development through qualitative investigation of phenomena in the same place as they occur. In this model, an approach is used for concept analysis that combines theoretical and empirical findings. Concept development using the hybrid model combines inductive and deductive methods and is thus able to refine concepts that have many applications. This model consists of three stages: the theoretical stage, the fieldwork stage, and the final analysis stage [18].
Theoretical Stage
A systematic approach was developed and implemented in the form of keyword selection, inclusion criteria, search strategy, study selection, data extraction, quality assessment, and data synthesis [19].
Through databases such as PubMed, PROQUEST, OVID, SCOPUS, WEB OF SCIENCE, CINAHL, Med-lib, SID, MagIran, Iran Doc, and Iran-Medex, a combination of keywords related to “distress,” “moral distress,” “ethics/morality,” “nursing/nurse,” “tools/instruments,” “questionnaires,” “pediatric nurse,” and “children” was utilized in both Persian and English for studies published from 2014 to 2024. This time period was chosen based on the nature of the research question and its meaning. An initial search yielded 640 articles. Articles that were unrelated to the main topic were filtered out based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, and the quality of the texts was assessed. The inclusion criteria for this study encompass sources that are (1) relevant to the study's objectives, (2) published in either Persian or English, (3) specifically related to the definitions, characteristics, facilitating and hindering factors, and consequences of the selected concept, and (4) published in peer-reviewed journals. Conversely, the exclusion criterion specifies that any studies for which the full text is not accessible will be omitted from the analysis. The quality of qualitative articles was assessed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) checklist, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA); quantitative articles were assessed using the Strengthening Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) tool. These tools were used to assess the quality of the articles included in the study, with a minimum score of 70% required to ensure their quality. Based on previous studies, the author considered this threshold to be a practical guide to minimize the inclusion of studies with significant methodological shortcomings and to increase the rigor of quality control of the articles. Subsequently, abstracts were assessed for relevance to the concept, followed by a thorough examination of full texts for eligibility and relevance to the study’s objective (Figure 1). A total of 15 English and Persian texts were selected and analyzed, comprising 5 studies in Persian and 10 in English. (Table 1).1
Ethics is an inseparable part of human life and a branch of applied philosophy that studies behaviors and ideal ways of life, seeking to discern what is right or wrong and to explain good and bad behaviors in specific situations [1]. The concept of moral distress, first introduced by Andrew Jameton in 1984 as painful psychological disequilibrium, has been discussed for over three decades [2]. Generally, moral distress can be defined as emotional and mental discomfort experienced when an individual, despite having the awareness and ability for moral judgment, commits a moral infraction due to actual or perceived limitations [3].
Moral distress, derived from nursing ethics, is defined as psychological distress arising when individuals are restricted from acting upon what they know is right [4]. Ethical challenges in nursing can manifest internationally in at least two forms: ethical dilemmas and moral distress [5]. Nursing, due to its nature, is a profession that encounters numerous ethical issues. Studies have demonstrated that experiencing moral distress causes harm to the individual and their affiliated organization [6]. Research indicates that moral distress leads to challenges for healthcare workers, including nurses [7-9]. Since pediatric nurses interact directly with patients and their parents, providing care requires nurses with appropriate ethical and scientific competencies [10]. Moral distress is a phenomenon discussed in nursing literature and in the pediatric context, but it is often considered absent from discussions in clinical practice. It is caused by disproportionate care associated with overtreatment. Nurses can present a variety of symptoms, characterizing moral distress as a highly subjective experience. The pediatric contexts of practice should promote a healthy, ethical climate and work towards a moral community built with peer support, education, communication, leadership, and management involvement [4]. Fachini and colleagues, in a study on pediatric intensive care nurses, identified a lack of technological resources and inhumane care as sources of low-quality care and moral distress. Interestingly, moral distress can similarly arise from inequitable resource distribution at local and global levels [11]. Nurses have identified painful clinical procedures, parents withholding the truth from children, poor team performance, lack of human resources, and insufficient time to address the needs of children and families as causes of moral distress [12].
Studies clearly highlight the devastating consequences of moral distress, such as burnout among nurses. Burnout is defined as emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion resulting from professional activities, leading to avoidance and depersonalization [4]. This can result in lower-quality care, job transfers, or even nurses leaving the profession altogether [4, 12].
To navigate the complexities of healthcare in pediatric wards and mitigate the damages caused by moral distress, pediatric nurses must recognize and address the moral distress in themselves and others. Studying and understanding this issue enhances the professional ethical values of nurses and provides them with the courage to advocate for the best interests of the child and family, independent of others’ opinions [13]. Therefore, studying moral distress among pediatric nurses reflects progress toward more humane and realistic care for children [4]. Although various studies have identified the severe consequences of moral distress for nurses [14] few have examined moral distress specifically among pediatric nurses. This highlights the need to organize the existing evidence on this concept within this community and a particular setting [4].
A review of previous studies shows that concept analysis of moral distress has been conducted in nursing specialties such as neuroscience nursing [5], critical care nursing [15], and midwifery [16]. Despite significant research on moral distress, no review on moral distress in nurses working in paediatric settings has been identified, which reinforces the need to map and organise the available evidence on this concept in this specific population and context. Additionally, Jameton alerts that it is still necessary to develop knowledge around this subject for its incoherencies [4]. Moral distress is still an ambiguous concept and inadequately supported by existing knowledge, necessitating the development of further understanding due to its inconsistencies [4, 17]. In this regard, the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACCN) recognizes moral distress as a complex and challenging concept, with the greatest difficulty lying in identifying this phenomenon [4]. Due to the lack of clarity regarding the various characteristics of moral distress across different settings, reflecting the fluid and context-dependent nature of this concept [6]. Given the lack of an appropriate empirical definition of the concept of "moral distress" among Iranian nurses working in pediatric wards, it is very important to understand the diverse perspectives of these nurses and clarify this concept.
Objective
This concept analysis aims to explore how nurses experience moral distress and identify its variations. Thus, the primary objective of this study is to present evidence on the concept of moral distress, its causes, symptoms, characteristics, consequences, and the strategies proposed by pediatric nurses, using a hybrid Schwartz-Barcott and Kim approach.
Methods
This research employed a hybrid concept analysis model based on Schwartz-Barcott and Kim’s approach. In this research, the concept of moral distress among pediatric nurses was analyzed using a hybrid model. It was chosen because the desired approach extracts the concept of knowledge in clinical practice, and the concept under study has a clinical aspect. The hybrid model is based on concept development through qualitative investigation of phenomena in the same place as they occur. In this model, an approach is used for concept analysis that combines theoretical and empirical findings. Concept development using the hybrid model combines inductive and deductive methods and is thus able to refine concepts that have many applications. This model consists of three stages: the theoretical stage, the fieldwork stage, and the final analysis stage [18].
Theoretical Stage
A systematic approach was developed and implemented in the form of keyword selection, inclusion criteria, search strategy, study selection, data extraction, quality assessment, and data synthesis [19].
Through databases such as PubMed, PROQUEST, OVID, SCOPUS, WEB OF SCIENCE, CINAHL, Med-lib, SID, MagIran, Iran Doc, and Iran-Medex, a combination of keywords related to “distress,” “moral distress,” “ethics/morality,” “nursing/nurse,” “tools/instruments,” “questionnaires,” “pediatric nurse,” and “children” was utilized in both Persian and English for studies published from 2014 to 2024. This time period was chosen based on the nature of the research question and its meaning. An initial search yielded 640 articles. Articles that were unrelated to the main topic were filtered out based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, and the quality of the texts was assessed. The inclusion criteria for this study encompass sources that are (1) relevant to the study's objectives, (2) published in either Persian or English, (3) specifically related to the definitions, characteristics, facilitating and hindering factors, and consequences of the selected concept, and (4) published in peer-reviewed journals. Conversely, the exclusion criterion specifies that any studies for which the full text is not accessible will be omitted from the analysis. The quality of qualitative articles was assessed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) checklist, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA); quantitative articles were assessed using the Strengthening Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) tool. These tools were used to assess the quality of the articles included in the study, with a minimum score of 70% required to ensure their quality. Based on previous studies, the author considered this threshold to be a practical guide to minimize the inclusion of studies with significant methodological shortcomings and to increase the rigor of quality control of the articles. Subsequently, abstracts were assessed for relevance to the concept, followed by a thorough examination of full texts for eligibility and relevance to the study’s objective (Figure 1). A total of 15 English and Persian texts were selected and analyzed, comprising 5 studies in Persian and 10 in English. (Table 1).1
The text of literature was analyzed using a conventional content analysis approach, following the proposed stages outlined by Graneheim and Lundman (2004). The full texts of the selected literature were read multiple times, line by line and paragraph by paragraph, to gain a deep understanding of the overall content and context. Segments of text relevant to the research question were selected as meaning units (words, sentences, or paragraphs containing aspects related to each other through their content and context). These meaning units were then condensed while preserving the core meaning. Condensed meaning units were labeled with initial codes that described their essential content. Codes were data-driven and remained close to the original. Similar codes were grouped into categories, reflecting shared patterns or topics within the data. These categories are more descriptive and remain close to the manifest content of the texts. categories were compared and abstracted into themes, which reflect a latent content or underlying meaning across multiple categories. Themes are interpretive and express the thread of meaning running through the data. Throughout this process, codes and categories were iteratively reviewed, revised, and merged where appropriate to ensure internal consistency [20]. 315 initial codes and 7 categories were extracted from the theoretical stage (Table 2)
Table 1. Key Evidence on Moral Distress (2014-2024)
| Author(s), Year, Country | Study Design / Method | Key Contributions to the Concept of Moral Distress | ||
| Antecedents (Causes/Triggers) | Attributes (Characteristics/Manifestations) | Consequences (Outcomes) | ||
| Sadooghiasl et al. [41]. (2018), Iran | Hybrid Concept Analysis | - Oppressive climate - Personal barriers (fear, risk) |
- Moral Courage: Moral self-actualization, managing fear, responsibility | - Professional excellence - Proper functioning of nurses - Peace of mind |
| Ventovaara et al [12]. (2021), Finland | Cross-sectional | - Disproportionate care - Inadequate resources - Poor teamwork & communication - Institutional policies |
- Anger, sadness, frustration - Powerlessness, helplessness |
- Positive: Moral resilience, improved care quality, job satisfaction - Negative: Burnout, intention to leave, poor teamwork |
| Tahmasebi et al. [42]. (2022), Iran | Cross-sectional | - Inability to bear costs of stopping treatment | - Inability to make clinical decisions | - Moral distress |
| Rebecca [5] (2024), UK | Integrated Mixed Research Synthesis | - Poor patient care & harm - Internal constraints (fear of conflict) - Supervisor relationship |
- Recognizing unethical circumstances but not acting | - Negative feelings - Coping mechanisms - Positive effects (e.g., moral courage) |
| Ghasemi et al. [43]. (2019), Iran | Cross-sectional | - Performing painful procedures on patients | - Psychological and emotional distress | - (Implied) Job-related stress |
| Topal et al. [44]. (2024), Turkey | Cross-sectional | - (Moral Distress as an antecedent) | - (Moral Distress as a phenomenon) | - Burnout - Reduced quality of care |
| Tajalli et al. [32]. (2021), Iran | Cross-sectional | - External & internal constraints | - Psychological suffering from inability to act | - Intention to quit the job |
| Deschenes et al. [30]. (2023), Canada | Qualitative Description | - (Focus on interventions) | - (Focus on interventions) | - Recommended Interventions: Support for nurses/families, improved communication, education |
| Soriano[45] (2022), USA | Descriptive Correlational | - Unhealthy ethical climate | - Experience of moral distress | - Intention to leave the profession |
| Chen et al. [46]. (2024), China | Scoping Review | - (Focus on coping strategies) | - Maladaptive Strategies: Passive acceptance, leave, drinking - Adaptive Strategies: Pursuing interests, reflection, communication |
- (Various coping outcomes) |
| Miranda et al. [4]. (2024), Portugal | Scoping Review | - Disproportionate care (overtreatment) | - Highly subjective experience with varied symptoms | - Recommended Context: Need for healthy ethical climate, peer support, education |
| Foster et al. [16]. (2022), Australia | Rodgers' Concept Analysis | - Clinical situations, moral awareness, uncertainty, constraint | - Moral actions/inactions, conflicting needs, negative feelings, powerlessness | - Adverse personal, professional, and organizational outcomes |
| Deschenes et al. [30]. (2020), Canada | Concept Clarification | - External: System/institutional constraints - Internal: Personal failings/weakness of will |
- (Inherent in the constraints) | - (Implied psychological distress) |
| Bagheri et al. [31]. (2023), Iran | Rodgers' Concept Analysis | - Individual, social, organizational, cultural factors | - Emotional/psychological pain, moral mistakes, failure to decide | - Physical & psychological impacts |
| Aljabery et al. [47]. (2024), South Africa | Integrative Review | 1. Experiencing a moral situation (e.g., conflicting values, team dynamics) 2. Presence of constraints (Individual, Team, System) |
1. Making a moral judgment 2. Moral wrongdoing (inability to act) 3. Moral suffering |
- Impacts on physical, emotional, and psychological well-being |
Table 2. Summary of Concept Analysis Findings: Themes and Categories from the Theoretical and Fieldwork Phases
| Phase | Domain | Main Themes / Categories | Subcategories / Manifestations |
| Theoretical Phase | Antecedents | Weak resource | Poor Teamwork and Communication Inadequate Human Resources and Equipment |
| Attributes | Moral temptation | Moral Dilemma Psychological Issues |
|
| Consequences | Conflicting emotions | Moral Courage Burnout Fear of Encountering Patients |
|
| Fieldwork Phase | Antecedents | Moral distress related to colleagues Moral distress related to organizational factors |
Moral distress related to physician colleagues Moral distress related to nurse colleagues Human resource shortages Lack of appropriate equipment |
| Consequences | Psychological tensions following moral distress | Mental engagement Burnout |
Fieldwork Phase
A qualitative approach utilizing conventional content analysis was chosen to achieve the study’s objectives [21]. Interviews were conducted by the researcher with 12 nurses. Purposeful sampling was employed for this study, meaning participants were selected from nurses working in pediatric wards who had experienced moral distress. Efforts were made to include nurses of different genders, marital status, education, and wards and hospitals to provide rich, extensive, and deep information through a maximum variation sampling strategy (Table 3).
Table 3. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Participants (N = 12)
A qualitative approach utilizing conventional content analysis was chosen to achieve the study’s objectives [21]. Interviews were conducted by the researcher with 12 nurses. Purposeful sampling was employed for this study, meaning participants were selected from nurses working in pediatric wards who had experienced moral distress. Efforts were made to include nurses of different genders, marital status, education, and wards and hospitals to provide rich, extensive, and deep information through a maximum variation sampling strategy (Table 3).
Table 3. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Participants (N = 12)
| Characteristic | Category | n |
| Gender | Male | 4 |
| Female | 8 | |
| Marital Status | Married | 10 |
| Single | 2 | |
| Education | Bachelor's | 10 |
| Master's | 2 | |
| Hospital Ward | Emergency | 5 |
| Surgery | 3 | |
| Infectious | 2 | |
| Oncology | 2 | |
| City | Babol | 4 |
| Tehran | 2 | |
| Hospital Type | Government | 6 |
| Private | 2 |
The sample size was determined based on data saturation. Data collection continued until a point was reached where further data collection resulted in repeating previous data with no new information emerging. Sampling continued until data saturation was reached, which was defined as conducting three consecutive interviews without extracting new codes or thematic insights. Semi-structured individual interviews were used as the primary method of data collection. Data collection began with participants filling out consent forms. The interviews commenced with open-ended questions such as, “Please describe your experiences during a shift in the pediatric ward. What ethical issues did you encounter while caring for a child? What factors during child care caused your moral distress?” Then, clarifying questions were used based on participants’ responses and the research goals. Examples of these questions were “What contributed to your moral distress?”, “What happened next?”, “Can you please explain more?” “What do you mean by this?”. The author conducted the interviews after introducing himself and the objectives of the study. Interviews were conducted at the request of the participants at the workplace. Data collection continued until the development of categories and data saturation. The length of the interviews was 32 minutes, on average. All interviews were held in a quiet room in the participants’ workplace and were recorded with their consent (Table 4).
Table 4. Example of Qualitative Data Analysis for Moral Distress Related to Colleagues
| Category | Sub-category | Primary Codes | Meaning Units (Participant Quotations) |
| Moral distress related to colleagues | Moral distress related to physician colleagues | • Physician's reprimand for sharing medical information with families • Disregard for nurses' clinical concerns • Patient harm due to physician's lack of technical skill • Denial of skill deficit despite negative outcomes • Psychological impact on nurse from preventable harm |
"I was in a private hospital. I had just entered the ward. I checked the patient's chart and informed the mother that her child would only need Pedialyte. The mother became angry, stating, 'I pay 5 million Tomans per night for this hotel...' The physician pulled me aside and said, 'You had no right to disclose medical information to the mother. Who do you think you are?'" "Sometimes, when a physician lacks proficiency in a procedure like intubation but insists on performing it, I intervene to prevent potential harm. However, they often dismiss my concerns due to hierarchical differences... We had a case where a failed intubation led to a child's death due to emphysema. That child's face still haunts me... This is moral distress." |
| Moral distress related to nurse colleagues | • Disregard for patient privacy • Patient and family distress due to repeated examinations • Unwillingness to delegate tasks to competent colleagues • Persistence in performing procedures despite fatigue • Risk of physical and psychological harm to patients from repeated attempts |
In this study, data analysis was conducted following the methods of Graneheim and Lundman (2004). Initially, each interview was transcribed by the researcher, who listened to the recordings multiple times to gain overall familiarity with the text.
Then, semantic units within the text were identified, and appropriate codes were extracted. With the repetition of interviews, extracted codes were compared based on similarities and differences and categorized under abstract labels. Finally, the categories were compared with subcategories, and through careful and in-depth reflection on them and the relevant data text, they were placed into suitable themes [20]. At this stage, 345 initial codes, 6 subcategories, and 3 categories were established (Table 2).
The four criteria of Guba and Lincoln’s: credibility, dependability, conformability, and transferability, were used for the consideration of rigour [22]. To increase credibility, the researcher had the appropriate communication and interaction with the participants. For the convergence of data with experience, the primary codes were checked by participants and corrections made wherever necessary. To ensure the confirmability of the data, two qualitative researchers checked the codes and the categories that emerged from the interviews. The researcher obtained the data and performed the interviews with the nurses by asking the latter probing questions based on the participants’ previous answers. Also, in the data analysis, she extracted the codes without personal bias. To ensure the dependability of the study results, methods utilised for coding concepts and themes, as well as textual and audio data, became available to researcher and specialists.
Furthermore, assessed and commented on the generated codes and categories. Sampling with maximum variation concerning participants’ gender, Marital status, Hospital, Ward, and educational level also helped ensure transferability (Table 3). There were also attempts to select the study sample completely based on the objectives of the study and without any bias.
Final Analysis Stage
In the final stage, the codes and themes obtained from the fieldwork stage were compared with the codes obtained from the literature review stage to provide a definitive and context-based definition of "moral distress."
In other words, after reviewing the literature in the theoretical stage, the characteristics, antecedents, and consequences of moral distress were identified for analyzing the concept of moral distress. In the fieldwork stage, it was also determined how the dimensions of moral distress characteristics occur in natural and real situations [23].
The extracted codes and the initial definition formed from the main concept; in the theoretical stage, they were compared with the empirical findings and, based on the results of the two previous stages, the proposed definition was reviewed, refined, and re-explained;
The data analysis showed that some of the characteristics obtained in the field presence stage were consistent with the theoretical stage. existing conflicts were resolved through negotiation, interaction, and cooperation, and a final agreement was reached, and finally, a more complete definition that included the key characteristics of the concept was presented.
To comply with ethical considerations in the theoretical stage, the research was conducted in accordance with the laws of the Republic of Iran; and in the debriefing stage, written and verbal consent was obtained from the participants to participate in the study and record their voices; and they were explained the purpose of the study, the confidentiality of the information, the anonymity of their names, and the right to withdraw from the research at any time.
Results
Theoretical Phase
In this phase, four main themes were identified: Features (properties), antecedents, and consequences of moral distress (Figure 2).
Characteristics and Definition of the Concept
Moral Dilemma
Moral distress arises from the conflict between professional and personal values and represents one of the challenges nurses face in various situations related to ethical decision-making. Moral distress occurs when an individual knows the right course of action, but organizational limitations or fear of consequences make it nearly impossible to do the right thing.
A moral dilemma is a situation in which the nurses are forced to choose between two options based on their equipment and facilities. In these situations, the nurses would hesitate between their internal conflicts and confusion between choosing their own benefits and the patients’ benefits. In these situations, nurses would also feel squeezed between self-authority and the demands of others, and they would try to resolve these conflicts.
At these crossroads, the nurses are faced with a shortage in equipment and facilities, and even human resources, which would cause them to face more conflicts in making ethical decisions [24].
Psychological Issues
A characteristic of psychological distress is that nurses experiencing moral distress often encounter psychological problems such as sadness, despair, and anxiety. The moral distress experienced by nurses in various situations can lead to feelings of failure and guilt, anger, job dissatisfaction, stress, displacement, sadness, anxiety, shame, low self-esteem, feelings of burnout, insecurity, fear, discouragement, and depression. These factors can severely impact their personal lives and professional performance [25].
Antecedents of the Concept
Poor Teamwork and Communication
Moral distress is often associated with factors at the unit/team level and the systemic level. When there is weak communication within the unit or insufficient collaboration among team members, moral distress can arise. Furthermore, staff-perceived insecurity or inefficiency is considered a contributing factor to moral distress [10]. Poor communication affecting patient care accounted for the second-highest average moral distress score in the group [5].
Inadequate Human Resources and Equipment
Various factors can contribute to the emergence of moral distress in nurses, such as shortages of human resources, available resources in clinical environments, low-quality care provided by physicians and nurses, medical errors and negligence, incompetency among colleagues, and conflicts between treatment teams [6]. Nurses identified painful procedures, parents misleading children, poor team dynamics, and lack of resources and time to meet the needs of children and families as causes of moral distress [12].
Consequences
The consequences of moral distress can manifest in two scenarios. On one side, an empowered nurse acts as a moral agent, confronting the situation, addressing it, and striving to be an advocate for oneself and others, resulting in a positive outcome such as moral resilience. On the other side, nurses may face “stagnation in ambiguity,” where a persistent sense of helplessness leads to passivity and resignation, which may be perceived as a norm. This situation creates challenges for supporting others and paves the way for passivity and the persistence of ethical impacts [26, 27].
Moral Courage
The nurse is viewed as a moral agent who embodies a pathway to positive outcomes and implies moral courage to do what they believe is right [4]. For this to materialize, every nurse needs to develop moral sensitivity, considered an acquired skill for developing ethical practice and competence [26, 27]. Concurrently, an ethical atmosphere focused on interprofessional interactions and organizational structures can serve as a promoting factor or a suppressive force in recognizing, discussing, and making decisions about ethical situations [28].
Burnout
Over time, moral distress can lead to dissatisfaction, burnout, and an intention to leave the profession among nurses [6]. Studies have clearly identified the devastating consequences of moral distress for nurses, such as burnout, defined as emotional, physical, and psychological exhaustion resulting from professional activities, leading to avoidance and depersonalization [4]. This can result in low-quality care, job changes, and departures from the nursing profession [4, 12]. Conversely, and more importantly, moral distress can inspire self-reflection for personal growth and support for the child and family [29, 30].
Fear of Encountering Patients
These consequences not only affect nurses but also impact patients, as nurses may provide poor and insufficient care, leading to prolonged hospital stays [6].
Moral distress is a factor that causes nurses to avoid patient encounters, further reducing the quality of care provided. The fear of facing patients is a serious and dangerous consequence of moral distress in such situations [6].
Hence, moral distress contributes to increased recovery times for patients, which in turn prolongs their hospital stays [28].
Fieldwork Stage
Out of the 12 participants in the research, there were 8 women and 4 men. Among them, 10 were specialists and 2 were senior specialists. The participants were divided into departments: 5 in the emergency department, 3 in surgery, 2 in infectious disease, and 2 in oncology. Additionally, 10 of them were married. From the rich and profound descriptions of these participants, 3 main categories and 6 subcategories were extracted, which are presented in Table 4.
1. Moral Distress Related to Colleagues
One of the perceptual themes from nurses in the pediatric ward is the moral distress associated with colleagues. Nurses expressed moral distress due to the lack of adequate skills from certain physicians, the potential harm to patients, and the irresponsibility of some nursing colleagues. This moral distress was classified into moral distress related to physicians and moral distress related to nurse colleagues.
Moral distress related to physician colleagues
This is one dimension of the concept of moral distress related to colleagues, indicating that most participants experienced moral distress due to unethical practices by physicians and insufficient skills in performing their jobs. Some participants reported feeling powerless and robotic due to unethical behavior by physicians, who would insult them for providing accurate information and education to parents about their child’s illness and medication.
In this regard, one participant stated:
“I was in a private hospital and had just entered the ward. I checked the medical chart and told the mother that her child only needed Pedialyte. The mother got angry, saying I pay 5 million a night for this hotel… The doctor pulled me aside and said, ‘You had no right to give the mother any medication information; who are you?’” (P8).
Nurses considered the lack of proper communication with doctors and being forced to obey the doctor as causes of moral distress.
Moral Distress Related to Nurse Colleagues
This is another dimension of the concept of moral distress related to colleagues, showing that nurses experience moral distress due to the irresponsibility and insufficient skills of some colleagues who insist on performing their duties.
Participants stated that nurses behave inappropriately with children due to fatigue from work and, in such conditions, are hesitant to entrust their tasks to colleagues, which can increase the likelihood of errors. Nurses highlighted the failure to respect the child’s privacy and confidentiality by the treatment team as one of the ethical issues and challenges in the pediatric department.
They noted that in such circumstances, where the child’s privacy should be respected and the child should be assured that their information remains confidential, no attention is given to this matter.
A participant’s experience supports this:
“A child was in the emergency department for two hours due to sexual misconduct. In the end, the child complained about why everyone was examining them. The child’s privacy was violated… No one paid attention to this. I was very affected; I couldn’t say anything. Everyone was discussing it, ‘Oh, this child…’ Everyone was looking.” (P6).
Lack of sufficient skills among colleagues in patient care and failure to respect patient privacy are among the issues that can lead to moral distress among nurses.
2. Moral Distress Related to Organizational Factors
The concept of moral distress related to organizational factors indicates that certain managerial factors and organizational policies can lead to moral distress in nurses. Nurses identified high workloads, staff shortages, and the lack of suitable and adequate equipment as causes of moral distress.
Human Resource Shortages
This dimension indicates that a lack of time and a high workload prevent the performance of certain tasks and cause moral distress among nurses. Participants mentioned that due to high workloads and staff shortages, they cannot attend to the emotional state of children and their families, feeling guilty for not addressing the ignorance and stress of parents.
In this regard, one participant stated:
“Professional ethics are not observed… The emotional state of the child or family is not considered… The high workload or excessive fatigue doesn’t allow for this… I feel guilty about it. I tell the family of the anxious child to stay behind the door; keep your voice down… This bothers me.” (P10).
Organizational factors, such as a lack of manpower and high workload, mean that nurses do not have enough time to pay attention to the psychological state of the child and family, and this can cause moral distress in nurses.
Lack of Appropriate Equipment
This is another aspect of moral distress related to organizational factors. This concept indicates that malfunctioning equipment, insufficient explanations regarding the operation of new devices from the responsible parties, and the absence of necessary medications contribute to moral distress in nurses.
One participant mentioned:
“Other departments call asking if we have this IV drip or medication. Because I know I have no backup, I unconsciously say we don’t have it. I must prioritize my department’s needs… But then I feel like I’ve betrayed them by lying.” (P11).
Lack of adequate equipment and facilities in the ward and failure to properly respond to the needs of colleagues in other departments can cause moral distress in nurses.
3. Psychological Tensions Following Moral Distress
This concept indicates that nurses experience tensions in the form of guilt, humiliation, helplessness, and desperation following moral distress. Mental engagement and burnout are characteristics of this concept.
Mental Engagement
This aspect of psychological tensions shows that nurses become preoccupied with issues when facing moral distress due to the ignorance and lack of attention from parents regarding their child, leading to anxiety.
A participant stated:
“The incident of a child falling through the rails and the negligence of the parents affected me a lot… I went home and put up barriers… I became so worried that I kept telling everyone what happened… I developed an internal stress. I kept thinking about it for a long time.” (P7).
Moral distress has consequences in the form of psychological stress, such as anxiety and mental conflict, for nurses.
Burnout
This is another aspect of psychological tensions following moral distress. Participants mentioned feeling helpless and desperate when witnessing colleagues making mistakes in medication administration and ignoring their suggestions.
In this context, one participant said:
“I often saw colleagues making mistakes with medication… I pointed it out, but no one paid attention. I felt helpless and desperate, knowing my voice wasn’t heard, and my suggestions were ignored. It didn’t matter… I studied a lot, did research, but it was useless.” (P11).
When nurses faced the sudden death of a newborn, they felt responsible and ineffective. They mentioned that when a newborn suddenly had an apnea despite being monitored and all appearing normal, they felt so bad that they preferred to take a few days off work to avoid being in the unit. They believed they were the cause of the child’s death.
Final Findings
At this stage, the final definition of “moral distress” among pediatric nurses was obtained by integrating the findings of both the theoretical and field phases. The theoretical phase involved a comprehensive review of the scientific literature to identify the characteristics, antecedents, and consequences of moral distress, which provided a solid conceptual foundation. Accordingly, nurses identified the roots of moral distress as poor communication and teamwork, involvement in unsafe care, inadequate working conditions, shortages of staff and equipment, and hierarchical structures. They attempted to come to terms with the status quo by using coping mechanisms such as avoidance. Nurses did not act on the unethical event at the time due to a combination of cognitive barriers, internal constraints, or institutional constraints. Internal constraints included conflict avoidance, relationship with supervisor, lack of self-confidence, feelings of inferiority, and lack of credibility. The nurse experiences negative emotions (sadness, hopelessness, self-blame, regret, guilt, negative stress, physical symptoms, psychological symptoms, anxiety, depression, loneliness, and quitting the profession). In addition to the initial negative emotions (reflexive emotions), positive consequences of moral distress, such as courage, may also be experienced. During the fieldwork phase, interviews with pediatric nurses provided valuable insights into moral distress. Mechanisms such as avoidance, self-blame, and pleasant cognitive reconstruction of events were identified that allow pediatric nurses to justify their helplessness in the face of unethical actions. The findings also suggest that these behaviors can be carried out to maintain job security, psychological safety, and individual and organizational satisfaction.
Furthermore, the antecedents, characteristics, and ultimate consequences of this concept can be described as follows:
The identified antecedents include “poor teamwork and communication” and “inadequate human resources and equipment,” all of which predispose nurses to moral distress. The characteristics of "moral distress," mentioned in both stages, include "moral dilemma" and "psychological difficulties." Finally, this study revealed several consequences of moral distress, including fear of patient confrontation, burnout about committing unethical acts, and moral courage. These consequences highlight the long-term effects of moral distress at both individual and organizational levels in healthcare settings.
Discussion
The analysis of the concept of moral distress in pediatric nurses has clarified this concept and has shown that it encompasses a range of characteristics, antecedents, and consequences. In this study, most of the findings from the theoretical phase were consistent with the findings from the practical, field phase. The present study indicates that moral distress is a subjective-objective experience. Moral distress arises when an individual’s moral integrity is seriously threatened, either because the individual feels unable to act according to core values and commitments, or because attempts made to achieve the desired outcome fail [31].
Moral distress is suffering that affects a person’s body, mind, and relationships when they are aware of what should be done, but are unable to do it due to circumstances [11]. Moral distress occurs when individuals have a clear moral judgment about the actions they should take, but are prevented from doing so due to institutional, social, or contextual limitations [32]. Studies emphasize a wide range of symptoms associated with moral distress, a multidimensional experience [4] that can have physical, emotional, and psychological effects on oneself and others [29]. As frontline workers, nurses face unique emotional and ethical challenges within the healthcare system. Their constant interaction with patients and families positions them as key witnesses to the systemic issues that contribute to moral distress. Many nurses’ concerns about inadequate resources and a lack of ethical education when making difficult decisions regarding life-sustaining treatments, end-of-life care, and complex family dynamics [33].
The findings of the present study indicated that organizational factors such as poor teamwork, a shortage of human resources and appropriate equipment, and a high workload are antecedents to the concept of moral distress. In this regard, the results of various studies showed that the work environment and organizational culture should be considered as factors that can play an effective role in creating moral distress. Nurses in Iran face ambiguities in job descriptions, heavy workloads, and a serious shortage of nursing staff, which affects their level of moral distress. In this context, nurses are assigned various tasks and responsibilities that do not allow them to engage in policy development and governance [6, 34].
Factors such as poor collaboration of the medical team and the presence of nurses who do not have sufficient control over the provision of care to patients can be effective in creating and exacerbating moral distress. Many studies have stated that team members and health service managers are often involved in problems related to patient care and treatment decisions. These issues may be related to economic or political factors existing in the medical center. On the other hand, the inability of nurses to demonstrate courageous behaviors in the medical team makes it difficult for them to communicate effectively with patients and other members of the treatment team. Therefore, they experience moral distress. Another study showed that increased risk of harm to patients and inadequate responsibilities of nurses can lead to increased moral distress in nurses and their colleagues [6]. Pressure imposed on nurses by organizations and institutional policies, working with incompetent colleagues, poor management, high workload, lack of facilities, and manpower are factors that can be effective in creating moral distress [32]. Situations identified as major sources of moral distress in pediatric nursing included performing procedures on children who resisted the treatment. Nurses were also short of time and had inadequate staffing levels, which prevented them from supporting families in the way they felt was needed [12]. Similarly, Newman et al. reported that failure to provide compassionate, high-quality care increased moral distress among pediatric nurses [28]. These findings are consistent with the findings of the present study, in which nurses mentioned that they could not resist some unethical requests from their physician colleagues. Given their vital position, the voices of nurses must be heard and integrated into conversations about systemic change. Nurses often occupy a lower position within the medical hierarchy, limiting their ability to advocate for improvements in working conditions and patient care. This lack of authority exacerbates feelings of moral distress, as nurses may feel their insights and concerns go unrecognized. Despite their extensive experience and knowledge of patient care challenges, they often navigate a system that prioritizes administrative decisions over clinical input. Therefore, actively including nurses in discussions about healthcare reform is not just beneficial; it is essential for fostering a responsive and effective healthcare environment [35].
The consequences of the concept of moral distress in pediatric nurses include both positive and negative dimensions. Nurses either deal with moral distress courageously, taking ethical and correct actions, or they suffer from symptoms such as fear, anxiety, hopelessness, helplessness, burnout, and reduced quality of care. Moral distress can lead to burnout, anger, sadness, hopelessness, job abandonment, withdrawal from patients, and reduced quality of care [28].
Internal ethical tensions indicate that nurses experience tensions following non-compliance with the patient’s privacy, the sudden death of the infant, and ignoring their abilities [28]. Some studies have reported the negative effects of ethical distress on the physical health of nurses in the form of night nightmares, insomnia, heart palpitations and neck pain, feelings of worthlessness, anger, depression, shame, and discomfort in their professional life [36]. Ignoring the causes of moral distress leads to negative consequences, such as the movement of nurses in departments, job abandonment, withdrawal from patients, reduced communication with other members of the treatment team, reduced organizational support, fear of legal consequences, job dissatisfaction, and reduced safety and quality of patient care [5]. These findings are in line with the findings of the present study, in which nurses felt upset and guilty following moral distress in the pediatric ward and preferred to take a period of time away from the ward and patient care. However, in the present study, in addition to negative experiences in the form of psychological tensions, nurses also had positive experiences, such as moral courage, in which nurses resisted inappropriate requests from doctors despite the prevailing medical hierarchy and responded to them with courage.
This difference could be due to some personality traits of some nurses and their unwillingness to give in to pressure.
The challenges and difficulties of ethical decision-making in specialized units, especially neonatal intensive care units, were another prominent theme. Staff working in neonatal intensive care units faced communication problems and ethical considerations that made nurses afraid of facing patients [37]. Nurses in pediatric wards faced barriers in effective pain management, fear of side effects, and difficulties in communicating with patients and families. These findings are supported by other studies conducted in this regard [38, 39].
The results of various studies show that people’s personal lives are affected by the negative symptoms of moral distress. When caregivers are unable to support a patient, they will have an uncomfortable and distressing feeling that, if repeated, will disrupt their adaptation, self-esteem, and ability to provide care [32, 40]. In these situations, they may use negative coping mechanisms and methods that affect the quality of patient care and create secondary complications. In addition, the results of some studies show that a nurse’s moral distress can be seen as an ethical factor and a way to achieve a positive outcome, implying moral courage to do what one believes is the right thing [4]. Participants in the present study experienced the negative dimension of moral distress as anxiety, fear, and feelings of helplessness.
Limitations of this study include not having access to all electronic data sources. The use of a qualitative approach in the fieldwork phase also limited the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusion
The results of this study emphasize the necessity and application of moral distress in nursing by explaining the concept of moral distress in pediatric nurses. The results of this study have implications for nursing practice, nursing education, and nursing research. The development of ethics committees comes, as well, as a strategy to offer support and understanding when ethical issues have risen within the team and/or between the team and family. It is well-recognised as the way to reach moral resilience and moral courage, professional satisfaction, and staff retention, and, more importantly, to improve the quality of the care provided. Familiarity with how to recognize ethical problems and distinguish between ethical problems and legal issues, knowledge of ethical principles, and awareness of the decision-making process are all useful and effective in having competent, ethical nurses who provide competent care. In this regard, holding various training courses to familiarize nurses and students with ethical concepts such as moral distress and moral courage, and providing solutions to resolve ethical dilemmas in clinical practice can be effective. Academic nurses can use these findings as evidence for revising the educational curriculum at the basic level of nursing and include ethical education. Nurse managers should also focus on available resources to prevent and address ethical distress. Nurses can experience less moral distress when the clinical environment enhances nurses' empowerment by encouraging them to share their experiences of ethical distress.
According to these findings, nursing leaders can create a supportive environment and omit suppressive factors, so that nurses can act with moral courage in the case of ethical issues. This study provides a basis for future research to raise the level of nurses’ moral courage.
Due to the fact that the concept of moral distress has been defined, it is recommended that further studies be conducted using diverse methodologies. Also, future qualitative research may aim to explore moral distress in nursing across diverse geographical and cultural settings to enrich the understanding of this phenomenon globally.
Ethical Considerations
The Ethics Committee of the Azad University of Babol, Iran, approved this study (code: IR.IAU.BABOL.REC.1402.115). All methods were carried out following relevant guidelines and regulations in the Ethical Declarations. Since all participants were over 16 years old, an informed consent letter was obtained from all participants before starting the study. After securing the participants’ consent, the interview sessions were recorded, and the researcher assured that the recording would be stopped at any participant’s request.
Participants were assured they could withdraw from the research at any time. Confidentiality of their identities was maintained, and results were presented to participants upon request, ensuring the utmost confidentiality.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the deputy of research of Islamic Azad University, Babol Branch, for supporting them in this study, and all the nurses who cooperated in the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Funding
None
Authors’ Contributions
Rahmani N: Supervised the analysis and research process, data analysis, and wrote the manuscript.
Artificial Intelligence Utilization for Article Writing
None
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available because individual privacy could be compromised. However, they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Then, semantic units within the text were identified, and appropriate codes were extracted. With the repetition of interviews, extracted codes were compared based on similarities and differences and categorized under abstract labels. Finally, the categories were compared with subcategories, and through careful and in-depth reflection on them and the relevant data text, they were placed into suitable themes [20]. At this stage, 345 initial codes, 6 subcategories, and 3 categories were established (Table 2).
The four criteria of Guba and Lincoln’s: credibility, dependability, conformability, and transferability, were used for the consideration of rigour [22]. To increase credibility, the researcher had the appropriate communication and interaction with the participants. For the convergence of data with experience, the primary codes were checked by participants and corrections made wherever necessary. To ensure the confirmability of the data, two qualitative researchers checked the codes and the categories that emerged from the interviews. The researcher obtained the data and performed the interviews with the nurses by asking the latter probing questions based on the participants’ previous answers. Also, in the data analysis, she extracted the codes without personal bias. To ensure the dependability of the study results, methods utilised for coding concepts and themes, as well as textual and audio data, became available to researcher and specialists.
Furthermore, assessed and commented on the generated codes and categories. Sampling with maximum variation concerning participants’ gender, Marital status, Hospital, Ward, and educational level also helped ensure transferability (Table 3). There were also attempts to select the study sample completely based on the objectives of the study and without any bias.
Final Analysis Stage
In the final stage, the codes and themes obtained from the fieldwork stage were compared with the codes obtained from the literature review stage to provide a definitive and context-based definition of "moral distress."
In other words, after reviewing the literature in the theoretical stage, the characteristics, antecedents, and consequences of moral distress were identified for analyzing the concept of moral distress. In the fieldwork stage, it was also determined how the dimensions of moral distress characteristics occur in natural and real situations [23].
The extracted codes and the initial definition formed from the main concept; in the theoretical stage, they were compared with the empirical findings and, based on the results of the two previous stages, the proposed definition was reviewed, refined, and re-explained;
The data analysis showed that some of the characteristics obtained in the field presence stage were consistent with the theoretical stage. existing conflicts were resolved through negotiation, interaction, and cooperation, and a final agreement was reached, and finally, a more complete definition that included the key characteristics of the concept was presented.
To comply with ethical considerations in the theoretical stage, the research was conducted in accordance with the laws of the Republic of Iran; and in the debriefing stage, written and verbal consent was obtained from the participants to participate in the study and record their voices; and they were explained the purpose of the study, the confidentiality of the information, the anonymity of their names, and the right to withdraw from the research at any time.
Results
Theoretical Phase
In this phase, four main themes were identified: Features (properties), antecedents, and consequences of moral distress (Figure 2).
Characteristics and Definition of the Concept
Moral Dilemma
Moral distress arises from the conflict between professional and personal values and represents one of the challenges nurses face in various situations related to ethical decision-making. Moral distress occurs when an individual knows the right course of action, but organizational limitations or fear of consequences make it nearly impossible to do the right thing.
A moral dilemma is a situation in which the nurses are forced to choose between two options based on their equipment and facilities. In these situations, the nurses would hesitate between their internal conflicts and confusion between choosing their own benefits and the patients’ benefits. In these situations, nurses would also feel squeezed between self-authority and the demands of others, and they would try to resolve these conflicts.
At these crossroads, the nurses are faced with a shortage in equipment and facilities, and even human resources, which would cause them to face more conflicts in making ethical decisions [24].
Psychological Issues
A characteristic of psychological distress is that nurses experiencing moral distress often encounter psychological problems such as sadness, despair, and anxiety. The moral distress experienced by nurses in various situations can lead to feelings of failure and guilt, anger, job dissatisfaction, stress, displacement, sadness, anxiety, shame, low self-esteem, feelings of burnout, insecurity, fear, discouragement, and depression. These factors can severely impact their personal lives and professional performance [25].
Antecedents of the Concept
Poor Teamwork and Communication
Moral distress is often associated with factors at the unit/team level and the systemic level. When there is weak communication within the unit or insufficient collaboration among team members, moral distress can arise. Furthermore, staff-perceived insecurity or inefficiency is considered a contributing factor to moral distress [10]. Poor communication affecting patient care accounted for the second-highest average moral distress score in the group [5].
Inadequate Human Resources and Equipment
Various factors can contribute to the emergence of moral distress in nurses, such as shortages of human resources, available resources in clinical environments, low-quality care provided by physicians and nurses, medical errors and negligence, incompetency among colleagues, and conflicts between treatment teams [6]. Nurses identified painful procedures, parents misleading children, poor team dynamics, and lack of resources and time to meet the needs of children and families as causes of moral distress [12].
Consequences
The consequences of moral distress can manifest in two scenarios. On one side, an empowered nurse acts as a moral agent, confronting the situation, addressing it, and striving to be an advocate for oneself and others, resulting in a positive outcome such as moral resilience. On the other side, nurses may face “stagnation in ambiguity,” where a persistent sense of helplessness leads to passivity and resignation, which may be perceived as a norm. This situation creates challenges for supporting others and paves the way for passivity and the persistence of ethical impacts [26, 27].
Moral Courage
The nurse is viewed as a moral agent who embodies a pathway to positive outcomes and implies moral courage to do what they believe is right [4]. For this to materialize, every nurse needs to develop moral sensitivity, considered an acquired skill for developing ethical practice and competence [26, 27]. Concurrently, an ethical atmosphere focused on interprofessional interactions and organizational structures can serve as a promoting factor or a suppressive force in recognizing, discussing, and making decisions about ethical situations [28].
Burnout
Over time, moral distress can lead to dissatisfaction, burnout, and an intention to leave the profession among nurses [6]. Studies have clearly identified the devastating consequences of moral distress for nurses, such as burnout, defined as emotional, physical, and psychological exhaustion resulting from professional activities, leading to avoidance and depersonalization [4]. This can result in low-quality care, job changes, and departures from the nursing profession [4, 12]. Conversely, and more importantly, moral distress can inspire self-reflection for personal growth and support for the child and family [29, 30].
Fear of Encountering Patients
These consequences not only affect nurses but also impact patients, as nurses may provide poor and insufficient care, leading to prolonged hospital stays [6].
Moral distress is a factor that causes nurses to avoid patient encounters, further reducing the quality of care provided. The fear of facing patients is a serious and dangerous consequence of moral distress in such situations [6].
Hence, moral distress contributes to increased recovery times for patients, which in turn prolongs their hospital stays [28].
Fieldwork Stage
Out of the 12 participants in the research, there were 8 women and 4 men. Among them, 10 were specialists and 2 were senior specialists. The participants were divided into departments: 5 in the emergency department, 3 in surgery, 2 in infectious disease, and 2 in oncology. Additionally, 10 of them were married. From the rich and profound descriptions of these participants, 3 main categories and 6 subcategories were extracted, which are presented in Table 4.
1. Moral Distress Related to Colleagues
One of the perceptual themes from nurses in the pediatric ward is the moral distress associated with colleagues. Nurses expressed moral distress due to the lack of adequate skills from certain physicians, the potential harm to patients, and the irresponsibility of some nursing colleagues. This moral distress was classified into moral distress related to physicians and moral distress related to nurse colleagues.
Moral distress related to physician colleagues
This is one dimension of the concept of moral distress related to colleagues, indicating that most participants experienced moral distress due to unethical practices by physicians and insufficient skills in performing their jobs. Some participants reported feeling powerless and robotic due to unethical behavior by physicians, who would insult them for providing accurate information and education to parents about their child’s illness and medication.
In this regard, one participant stated:
“I was in a private hospital and had just entered the ward. I checked the medical chart and told the mother that her child only needed Pedialyte. The mother got angry, saying I pay 5 million a night for this hotel… The doctor pulled me aside and said, ‘You had no right to give the mother any medication information; who are you?’” (P8).
Nurses considered the lack of proper communication with doctors and being forced to obey the doctor as causes of moral distress.
Moral Distress Related to Nurse Colleagues
This is another dimension of the concept of moral distress related to colleagues, showing that nurses experience moral distress due to the irresponsibility and insufficient skills of some colleagues who insist on performing their duties.
Participants stated that nurses behave inappropriately with children due to fatigue from work and, in such conditions, are hesitant to entrust their tasks to colleagues, which can increase the likelihood of errors. Nurses highlighted the failure to respect the child’s privacy and confidentiality by the treatment team as one of the ethical issues and challenges in the pediatric department.
They noted that in such circumstances, where the child’s privacy should be respected and the child should be assured that their information remains confidential, no attention is given to this matter.
A participant’s experience supports this:
“A child was in the emergency department for two hours due to sexual misconduct. In the end, the child complained about why everyone was examining them. The child’s privacy was violated… No one paid attention to this. I was very affected; I couldn’t say anything. Everyone was discussing it, ‘Oh, this child…’ Everyone was looking.” (P6).
Lack of sufficient skills among colleagues in patient care and failure to respect patient privacy are among the issues that can lead to moral distress among nurses.
2. Moral Distress Related to Organizational Factors
The concept of moral distress related to organizational factors indicates that certain managerial factors and organizational policies can lead to moral distress in nurses. Nurses identified high workloads, staff shortages, and the lack of suitable and adequate equipment as causes of moral distress.
Human Resource Shortages
This dimension indicates that a lack of time and a high workload prevent the performance of certain tasks and cause moral distress among nurses. Participants mentioned that due to high workloads and staff shortages, they cannot attend to the emotional state of children and their families, feeling guilty for not addressing the ignorance and stress of parents.
In this regard, one participant stated:
“Professional ethics are not observed… The emotional state of the child or family is not considered… The high workload or excessive fatigue doesn’t allow for this… I feel guilty about it. I tell the family of the anxious child to stay behind the door; keep your voice down… This bothers me.” (P10).
Organizational factors, such as a lack of manpower and high workload, mean that nurses do not have enough time to pay attention to the psychological state of the child and family, and this can cause moral distress in nurses.
Lack of Appropriate Equipment
This is another aspect of moral distress related to organizational factors. This concept indicates that malfunctioning equipment, insufficient explanations regarding the operation of new devices from the responsible parties, and the absence of necessary medications contribute to moral distress in nurses.
One participant mentioned:
“Other departments call asking if we have this IV drip or medication. Because I know I have no backup, I unconsciously say we don’t have it. I must prioritize my department’s needs… But then I feel like I’ve betrayed them by lying.” (P11).
Lack of adequate equipment and facilities in the ward and failure to properly respond to the needs of colleagues in other departments can cause moral distress in nurses.
3. Psychological Tensions Following Moral Distress
This concept indicates that nurses experience tensions in the form of guilt, humiliation, helplessness, and desperation following moral distress. Mental engagement and burnout are characteristics of this concept.
Mental Engagement
This aspect of psychological tensions shows that nurses become preoccupied with issues when facing moral distress due to the ignorance and lack of attention from parents regarding their child, leading to anxiety.
A participant stated:
“The incident of a child falling through the rails and the negligence of the parents affected me a lot… I went home and put up barriers… I became so worried that I kept telling everyone what happened… I developed an internal stress. I kept thinking about it for a long time.” (P7).
Moral distress has consequences in the form of psychological stress, such as anxiety and mental conflict, for nurses.
Burnout
This is another aspect of psychological tensions following moral distress. Participants mentioned feeling helpless and desperate when witnessing colleagues making mistakes in medication administration and ignoring their suggestions.
In this context, one participant said:
“I often saw colleagues making mistakes with medication… I pointed it out, but no one paid attention. I felt helpless and desperate, knowing my voice wasn’t heard, and my suggestions were ignored. It didn’t matter… I studied a lot, did research, but it was useless.” (P11).
When nurses faced the sudden death of a newborn, they felt responsible and ineffective. They mentioned that when a newborn suddenly had an apnea despite being monitored and all appearing normal, they felt so bad that they preferred to take a few days off work to avoid being in the unit. They believed they were the cause of the child’s death.
Final Findings
At this stage, the final definition of “moral distress” among pediatric nurses was obtained by integrating the findings of both the theoretical and field phases. The theoretical phase involved a comprehensive review of the scientific literature to identify the characteristics, antecedents, and consequences of moral distress, which provided a solid conceptual foundation. Accordingly, nurses identified the roots of moral distress as poor communication and teamwork, involvement in unsafe care, inadequate working conditions, shortages of staff and equipment, and hierarchical structures. They attempted to come to terms with the status quo by using coping mechanisms such as avoidance. Nurses did not act on the unethical event at the time due to a combination of cognitive barriers, internal constraints, or institutional constraints. Internal constraints included conflict avoidance, relationship with supervisor, lack of self-confidence, feelings of inferiority, and lack of credibility. The nurse experiences negative emotions (sadness, hopelessness, self-blame, regret, guilt, negative stress, physical symptoms, psychological symptoms, anxiety, depression, loneliness, and quitting the profession). In addition to the initial negative emotions (reflexive emotions), positive consequences of moral distress, such as courage, may also be experienced. During the fieldwork phase, interviews with pediatric nurses provided valuable insights into moral distress. Mechanisms such as avoidance, self-blame, and pleasant cognitive reconstruction of events were identified that allow pediatric nurses to justify their helplessness in the face of unethical actions. The findings also suggest that these behaviors can be carried out to maintain job security, psychological safety, and individual and organizational satisfaction.
Furthermore, the antecedents, characteristics, and ultimate consequences of this concept can be described as follows:
The identified antecedents include “poor teamwork and communication” and “inadequate human resources and equipment,” all of which predispose nurses to moral distress. The characteristics of "moral distress," mentioned in both stages, include "moral dilemma" and "psychological difficulties." Finally, this study revealed several consequences of moral distress, including fear of patient confrontation, burnout about committing unethical acts, and moral courage. These consequences highlight the long-term effects of moral distress at both individual and organizational levels in healthcare settings.
Discussion
The analysis of the concept of moral distress in pediatric nurses has clarified this concept and has shown that it encompasses a range of characteristics, antecedents, and consequences. In this study, most of the findings from the theoretical phase were consistent with the findings from the practical, field phase. The present study indicates that moral distress is a subjective-objective experience. Moral distress arises when an individual’s moral integrity is seriously threatened, either because the individual feels unable to act according to core values and commitments, or because attempts made to achieve the desired outcome fail [31].
Moral distress is suffering that affects a person’s body, mind, and relationships when they are aware of what should be done, but are unable to do it due to circumstances [11]. Moral distress occurs when individuals have a clear moral judgment about the actions they should take, but are prevented from doing so due to institutional, social, or contextual limitations [32]. Studies emphasize a wide range of symptoms associated with moral distress, a multidimensional experience [4] that can have physical, emotional, and psychological effects on oneself and others [29]. As frontline workers, nurses face unique emotional and ethical challenges within the healthcare system. Their constant interaction with patients and families positions them as key witnesses to the systemic issues that contribute to moral distress. Many nurses’ concerns about inadequate resources and a lack of ethical education when making difficult decisions regarding life-sustaining treatments, end-of-life care, and complex family dynamics [33].
The findings of the present study indicated that organizational factors such as poor teamwork, a shortage of human resources and appropriate equipment, and a high workload are antecedents to the concept of moral distress. In this regard, the results of various studies showed that the work environment and organizational culture should be considered as factors that can play an effective role in creating moral distress. Nurses in Iran face ambiguities in job descriptions, heavy workloads, and a serious shortage of nursing staff, which affects their level of moral distress. In this context, nurses are assigned various tasks and responsibilities that do not allow them to engage in policy development and governance [6, 34].
Factors such as poor collaboration of the medical team and the presence of nurses who do not have sufficient control over the provision of care to patients can be effective in creating and exacerbating moral distress. Many studies have stated that team members and health service managers are often involved in problems related to patient care and treatment decisions. These issues may be related to economic or political factors existing in the medical center. On the other hand, the inability of nurses to demonstrate courageous behaviors in the medical team makes it difficult for them to communicate effectively with patients and other members of the treatment team. Therefore, they experience moral distress. Another study showed that increased risk of harm to patients and inadequate responsibilities of nurses can lead to increased moral distress in nurses and their colleagues [6]. Pressure imposed on nurses by organizations and institutional policies, working with incompetent colleagues, poor management, high workload, lack of facilities, and manpower are factors that can be effective in creating moral distress [32]. Situations identified as major sources of moral distress in pediatric nursing included performing procedures on children who resisted the treatment. Nurses were also short of time and had inadequate staffing levels, which prevented them from supporting families in the way they felt was needed [12]. Similarly, Newman et al. reported that failure to provide compassionate, high-quality care increased moral distress among pediatric nurses [28]. These findings are consistent with the findings of the present study, in which nurses mentioned that they could not resist some unethical requests from their physician colleagues. Given their vital position, the voices of nurses must be heard and integrated into conversations about systemic change. Nurses often occupy a lower position within the medical hierarchy, limiting their ability to advocate for improvements in working conditions and patient care. This lack of authority exacerbates feelings of moral distress, as nurses may feel their insights and concerns go unrecognized. Despite their extensive experience and knowledge of patient care challenges, they often navigate a system that prioritizes administrative decisions over clinical input. Therefore, actively including nurses in discussions about healthcare reform is not just beneficial; it is essential for fostering a responsive and effective healthcare environment [35].
The consequences of the concept of moral distress in pediatric nurses include both positive and negative dimensions. Nurses either deal with moral distress courageously, taking ethical and correct actions, or they suffer from symptoms such as fear, anxiety, hopelessness, helplessness, burnout, and reduced quality of care. Moral distress can lead to burnout, anger, sadness, hopelessness, job abandonment, withdrawal from patients, and reduced quality of care [28].
Internal ethical tensions indicate that nurses experience tensions following non-compliance with the patient’s privacy, the sudden death of the infant, and ignoring their abilities [28]. Some studies have reported the negative effects of ethical distress on the physical health of nurses in the form of night nightmares, insomnia, heart palpitations and neck pain, feelings of worthlessness, anger, depression, shame, and discomfort in their professional life [36]. Ignoring the causes of moral distress leads to negative consequences, such as the movement of nurses in departments, job abandonment, withdrawal from patients, reduced communication with other members of the treatment team, reduced organizational support, fear of legal consequences, job dissatisfaction, and reduced safety and quality of patient care [5]. These findings are in line with the findings of the present study, in which nurses felt upset and guilty following moral distress in the pediatric ward and preferred to take a period of time away from the ward and patient care. However, in the present study, in addition to negative experiences in the form of psychological tensions, nurses also had positive experiences, such as moral courage, in which nurses resisted inappropriate requests from doctors despite the prevailing medical hierarchy and responded to them with courage.
This difference could be due to some personality traits of some nurses and their unwillingness to give in to pressure.
The challenges and difficulties of ethical decision-making in specialized units, especially neonatal intensive care units, were another prominent theme. Staff working in neonatal intensive care units faced communication problems and ethical considerations that made nurses afraid of facing patients [37]. Nurses in pediatric wards faced barriers in effective pain management, fear of side effects, and difficulties in communicating with patients and families. These findings are supported by other studies conducted in this regard [38, 39].
The results of various studies show that people’s personal lives are affected by the negative symptoms of moral distress. When caregivers are unable to support a patient, they will have an uncomfortable and distressing feeling that, if repeated, will disrupt their adaptation, self-esteem, and ability to provide care [32, 40]. In these situations, they may use negative coping mechanisms and methods that affect the quality of patient care and create secondary complications. In addition, the results of some studies show that a nurse’s moral distress can be seen as an ethical factor and a way to achieve a positive outcome, implying moral courage to do what one believes is the right thing [4]. Participants in the present study experienced the negative dimension of moral distress as anxiety, fear, and feelings of helplessness.
Limitations of this study include not having access to all electronic data sources. The use of a qualitative approach in the fieldwork phase also limited the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusion
The results of this study emphasize the necessity and application of moral distress in nursing by explaining the concept of moral distress in pediatric nurses. The results of this study have implications for nursing practice, nursing education, and nursing research. The development of ethics committees comes, as well, as a strategy to offer support and understanding when ethical issues have risen within the team and/or between the team and family. It is well-recognised as the way to reach moral resilience and moral courage, professional satisfaction, and staff retention, and, more importantly, to improve the quality of the care provided. Familiarity with how to recognize ethical problems and distinguish between ethical problems and legal issues, knowledge of ethical principles, and awareness of the decision-making process are all useful and effective in having competent, ethical nurses who provide competent care. In this regard, holding various training courses to familiarize nurses and students with ethical concepts such as moral distress and moral courage, and providing solutions to resolve ethical dilemmas in clinical practice can be effective. Academic nurses can use these findings as evidence for revising the educational curriculum at the basic level of nursing and include ethical education. Nurse managers should also focus on available resources to prevent and address ethical distress. Nurses can experience less moral distress when the clinical environment enhances nurses' empowerment by encouraging them to share their experiences of ethical distress.
According to these findings, nursing leaders can create a supportive environment and omit suppressive factors, so that nurses can act with moral courage in the case of ethical issues. This study provides a basis for future research to raise the level of nurses’ moral courage.
Due to the fact that the concept of moral distress has been defined, it is recommended that further studies be conducted using diverse methodologies. Also, future qualitative research may aim to explore moral distress in nursing across diverse geographical and cultural settings to enrich the understanding of this phenomenon globally.
Ethical Considerations
The Ethics Committee of the Azad University of Babol, Iran, approved this study (code: IR.IAU.BABOL.REC.1402.115). All methods were carried out following relevant guidelines and regulations in the Ethical Declarations. Since all participants were over 16 years old, an informed consent letter was obtained from all participants before starting the study. After securing the participants’ consent, the interview sessions were recorded, and the researcher assured that the recording would be stopped at any participant’s request.
Participants were assured they could withdraw from the research at any time. Confidentiality of their identities was maintained, and results were presented to participants upon request, ensuring the utmost confidentiality.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the deputy of research of Islamic Azad University, Babol Branch, for supporting them in this study, and all the nurses who cooperated in the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Funding
None
Authors’ Contributions
Rahmani N: Supervised the analysis and research process, data analysis, and wrote the manuscript.
Artificial Intelligence Utilization for Article Writing
None
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available because individual privacy could be compromised. However, they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Type of Study: Orginal research |
Subject:
Nursing
References
1. 1. Breen KJ. Medical Professionalism: Is It Really Under Threat? Medical Journal of Australia. 2007;186(11):596-8. [https://doi.org/10.5694/j.1326-5377.2007.tb01062.x] [PMID]
2. Schaefer R, Zoboli EL, Vieira MM. Psychometric Evaluation of the Moral Distress Risk Scale: A Methodological Study. Nursing Ethics. 2019;26(2):434-42. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733017707347] [PMID]
3. Nathaniel AK. Moral Reckoning in Nursing. Western Journal of Nursing Research. 2006;28(4):419-38. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0193945905284727] [PMID]
4. Miranda ACR, Fernandes SD, Ramos S, Nunes E, Fabri J, Caldeira S, editors. Moral Distress of Nurses Working in Paediatric Healthcare Settings. Healthcare. 2024;12(13):1364. [https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12131364] [PMID]
5. Rebecca T. Student Nurses Experiences of Moral Distress: A Concept Analysis. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2024;81(2):730-48. [https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.16370] [PMID]
6. Soleimani MA, Sharif SP, Yaghoobzadeh A, Panarello B. Psychometric Evaluation of the Moral Distress Scale-Revised Among Iranian Nurses. Nursing Ethics. 2019;26(4):1226-42. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733016651129] [PMID]
7. Brazil K, Kassalainen S, Ploeg J, Marshall D. Moral Distress Experienced by Health Care Professionals Who Provide Home-Based Palliative Care. Social Science & Medicine. 2010;71(9):1687-91. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2010.07.032] [PMID]
8. Borhani F, Mohammadi S, Roshanzadeh M. Moral Distress and Perception of Futile Care in Intensive Care Nurses. Journal of Medical Ethics and History of Medicine. 2015;8:2. PMID: 26839676
9. Sarkoohijabalbarezi Z, Ghodousi A, Davaridolatabadi E. The Relationship Between Professional Autonomy and Moral Distress Among Nurses Working in Children's Units and Pediatric Intensive Care Wards. International Journal of Nursing Sciences. 2017;4(2):117-21. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2017.03.004] [PMID]
10. Rahmani N, Seyed Nematollah Roshan F, Nabavian M, Firouzbakht M. Exploring the Experiences of Nurses Working in Pediatric Units Regarding Moral Distress: A Phenomenological Study. Nursing And Midwifery Journal. 2024;22(5):352-64. [https://doi.org/10.61186/unmf.22.5.352]
11. Fachini JS, Scrigni AV, Lima RdCGS. Sufrimiento Moral de Los Trabajadores de Una UCI Pediátrica [Moral Suffering of Workers in a Pediatric ICU]. Revista Bioética. 2017;25:111-22. [https://doi.org/10.1590/1983-80422017251172]
12. Ventovaara P, Sandeberg M, Räsänen J, Pergert P. Ethical Climate and Moral Distress in Pediatric Oncology Nursing. Nursing Ethics. 2021;28(6):1061-72. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733021994169] [PMID]
13. Falco-Pegueroles A, Lluch-Canut T, Roldan-Merino J, Goberna-Tricas J, Guardia-Olmos J. Ethical Conflict in Critical Care Nursing: Correlation Between Exposure and Types. Nursing Ethics. 2015;22(5):594-607. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733014549883] [PMID]
14. Deschenes S, Kunyk D. Situating Moral Distress Within Relational Ethics. Nursing Ethics. 2020;27(3):767-77. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733019884621] [PMID]
15. Cooke S, Booth R, Jackson K, editors. Moral Distress in Critical Care Nursing Practice: A Concept Analysis. Nursing Forum. 2022;57(6):1478-83. [https://doi.org/10.1111/nuf.12786] [PMID]
16. Foster W, McKellar L, Fleet J, Sweet L. Moral Distress in Midwifery Practice: A Concept Analysis. Nursing Ethics. 2022;29(2):364-83. [https://doi.org/10.1177/09697330211023983] [PMID]
17. Jameton A. What Moral Distress in Nursing History Could Suggest About the Future of Health Care. AMA Journal of Ethics. 2017;19(6):617-28. [https://doi.org/10.1001/journalofethics.2017.19.6.mhst1-1706] [PMID]
18. Schwartz-Barcott D. An Expansion and Elaboration of the Hybrid Model of Concept Development. In: Rodgers BL, Knafl KA, editors. Concept Development in Nursing: Foundations, Techniques, and Applications. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 2000. p. 129-59.
19. Briscoe S. Web Searching for Systematic Reviews: A Case Study of Reporting Standards in the UK Health Technology Assessment Program. BMC Research Notes. 2015;8:1-7. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-015-1079-y] [PMID]
20. Graneheim UH, Lundman B. Qualitative Content Analysis in Nursing Research: Concepts, Procedures and Measures to Achieve Trustworthiness. Nurse Education Today. 2004;24(2):105-12. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2003.10.001] [PMID]
21. Grove SK, Gray JR. Understanding Nursing Research: First South Asia Edition, E-Book: Building an Evidence-Based Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2019. p. 77-9.
22. Polit DF, Beck CT. Essentials of Nursing Research: Appraising Evidence for Nursing Practice. 7th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010. p. 79.
23. Schwartz BD, Kim HS. An Expansion and Elaboration of the Hybrid Model of Concept Development. In: Concept Development in Nursing: Foundations, Techniques, and Applications. 2000. p. 161-92.
24. Asadi N, Royani Z, Maazallahi M, Salmani F. Being Torn by Inevitable Moral Dilemma: Experiences of ICU Nurses. BMC Medical Ethics. 2021;22(1):159. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-021-00727-y] [PMID]
25. Ghafouri R, Lotfi-Bajestani S, Nasiri M, Ohnishi K, Atashzadeh-Shoorideh F. Psychometrics of the Moral Distress Scale in Iranian Mental Health Nurses. BMC Nursing. 2021;20(1):166. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-021-00674-4] [PMID]
26. Pergert P, Bartholdson C, Blomgren K, af Sandeberg M. Moral Distress in Pediatric Oncology: Contributing Factors and Group Differences. Nursing Ethics. 2019;26(7-8):2351-63. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733018809806] [PMID]
27. Welborn A. Moral Distress of Nurses Surrounding Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome: Application of a Theoretical Framework. Nursing Forum. 2019;54(4):644-52. [https://doi.org/10.1111/nuf.12362] [PMID]
28. Giannetta N, Villa G, Bonetti L, Dionisi S, Pozza A, Rolandi S, et al. Moral Distress Scores of Nurses Working in Intensive Care Units for Adults Using Corley's Scale: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022;19(17):10640. [https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710640] [PMID]
29. Rodney PA. What We Know About Moral Distress. American Journal of Nursing. 2017;117(2):S7-S10. [https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NAJ.0000512204.85973.04] [PMID]
30. Deschenes S, Scott SD, Kunyk D, editors. Mitigating Moral Distress: Pediatric Critical Care Nurses' Recommendations. HEC Forum. 2024;36(1):75-92. [https://doi.org/10.1007/s10730-023-09506-1] [PMID]
31. Bagheri F, Aghebati N, Heydari A. The Concept of Moral Distress in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: A Concept Analysis Using Rogers' Evolutionary Method. Education and Ethics In Nursing. 2023;11(3-4):50-60. [https://doi.org/10.22034/ethic.2023.703956]
32. Tajalli S, Rostamli S, Dezvaree N, Shariat M, Kadivar M. Moral Distress Among Iranian Neonatal Intensive Care Units' Health Care Providers: A Multi-Center Cross Sectional Study. Journal of Medical Ethics and History of Medicine. 2021;14:12. [https://doi.org/10.18502/jmehm.v14i12.7667] [PMID]
33. De Brasi EL, Giannetta N, Ercolani S, Gandini ELM, Moranda D, Villa G, et al. Nurses' Moral Distress in End-of-Life Care: A Qualitative Study. Nursing Ethics. 2021;28(5):614-27. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733020964859] [PMID]
34. Ghafouri R, Lotfi-Bajestani S, Nasiri M, Ohnishi K, Atashzadeh-Shoorideh F. Psychometrics of the Moral Distress Scale in Iranian Mental Health Nurses. BMC Nursing. 2021;20:166. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-021-00674-4] [PMID]
35. Mandrell B, Boggs J, Gattuso J, Caples M, Sawyer KE, Madni A, et al. Moral Distress and Moral Stress Among Nurses Facing Challenges in a Health Care System Under Pressure. American Journal of Bioethics. 2024;24(12):48-51.
https://doi.org/10.1080/15265161.2024.2417992 [https://doi.org/10.1080/15265161.2024.1869509] [PMID]
36. Kızıltepe SK, Koç Z. Exploring Moral Distress, Related Factors and Coping in Emergency Nurses: A Mixed Method Study. Nursing Open. 2025;12(1):e70141. [https://doi.org/10.1002/nop2.70141] [PMID]
37. Mitchell S, Spry JL, Hill E, Coad J, Dale J, Plunkett A. Parental Experiences of End of Life Care Decision-Making for Children With Life-Limiting Conditions in the Paediatric Intensive Care Unit: A Qualitative Interview Study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(5):e028548. [https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028548] [PMID]
38. Wuni A, Salia SM, Mohammed Ibrahim M, Iddriss I, Abena Nyarko B, Nabila Seini S, et al. Evaluating Knowledge, Practices, and Barriers of Paediatric Pain Management among Nurses in a Tertiary Health Facility in the Northern Region of Ghana: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study. Pain Research and Management. 2020;2020:8846599. [https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8846599] [PMID]
39. Alotaibi K, Higgins I, Day J, Chan S. Paediatric Pain Management: Knowledge, Attitudes, Barriers and Facilitators Among Nurses-Integrative Review. International Nursing Review. 2018;65(4):524-33. [https://doi.org/10.1111/inr.12465] [PMID]
40. Lewis SL. Emotional Intelligence in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Nurses: Decreasing Moral Distress in End-of-Life Care and Laying a Foundation for Improved Outcomes: An Integrative Review. Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing. 2019;21(4):250-6. [https://doi.org/10.1097/NJH.0000000000000561] [PMID]
41. Sadooghiasl A, Parvizy S, Ebadi A. Concept Analysis of Moral Courage in Nursing: A Hybrid Model. Nursing Ethics. 2018;25(1):6-19. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733016638146] [PMID]
42. Tahmasebi S, Sabeti F, Hagani H, Mohammadi R. Investigating the Relationship Between Clinical Decision Making and Moral Distress of Nurses Working in Pediatric Intensive Care Unit. Nursing And Midwifery Journal. 2022;20(2):137-46. [https://doi.org/10.52547/unmf.20.2.137]
43. Ghasemi E, Negarandeh R, Janani L. Moral Distress in Iranian Pediatric Nurses. Nursing Ethics. 2019;26(3):663-73. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0969733017722824] [PMID]
44. Topal S, Çaka SY, Öztürkler S, Gürbüz Y. Burnout in Pediatric Nurses: Examining the Relationship Between Moral Distress and Missed Nursing Care. Journal of Pediatric Nursing. 2024;78:e404-e10. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedn.2024.08.001] [PMID]
45. Bliss Soriano K. Moral Distress and Ethical Climate in Pediatric Nurses in the Time of COVID [dissertation]. 2022. p. 2-12.
46. Chen J, Lin N, Ye X, Chen Y, Wang Y, Xu H. Coping Strategies and Interventions to Alleviate Moral Distress Among Pediatric ICU Nurses: A Scoping Review. Nursing Ethics. 2024;32(2):437-59. [https://doi.org/10.1177/09697330241252875] [PMID]
47. Aljabery M, Coetzee-Prinsloo I, van der Wath A, Al-Hmaimat N. Characteristics of Moral Distress from Nurses' Perspectives: An Integrative Review. International Journal of Nursing Sciences. 2024;11(5):578-85. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2024.10.005] [PMID]
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |




