
Preventive Care in Nursing and Midwifery Journal

Volume 15, Issue 1 (1-2025)
Prev Care Nurs Midwifery J 2025, 15(1): 67-76 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: IR.IAU.Z.REC.1403.047
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Ahmadi M S, Masoomi Jahandizi H, Mohammadloo M, Alinejad M. Predicting the propensity for infidelity based on quality of life and emotional literacy with the mediating role of resilience in nurses. Prev Care Nurs Midwifery J 2025; 15 (1) :67-76
URL: http://nmcjournal.zums.ac.ir/article-1-950-en.html
URL: http://nmcjournal.zums.ac.ir/article-1-950-en.html
PhD in educational psychology, Assistant Professor, Department of Psychology and Counseling, Farhangian University, Tehran, Iran , ghavaghy57@cfu.ac.ir
Abstract: (996 Views)
Background: Marital infidelity is a complex marital trauma associated with numerous psychological and social consequences. Due to occupational pressures and specific working conditions, nurses may be at a higher risk of experiencing this phenomenon.
Objectives: The present study aimed to predict the propensity for infidelity based on quality of life and emotional literacy, with resilience serving as a mediating role in nurses.
Methods: This descriptive correlational study, based on structural equation modeling (SEM), was conducted on 265 nurses in 2023-2024. Participants were recruited using a convenience sampling method. Data were collected using the Scale of Marital Infidelity (Bashirpour et al.), the Medical Outcomes Study (MOS) 36-item, Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36) (Ware & Sherbourne), the Emotional Literacy Scale (Kimiyaee), and the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC). Data were analyzed using Pearson’s correlation in SPSS version 25 and SEM in LISREL version 8.8.
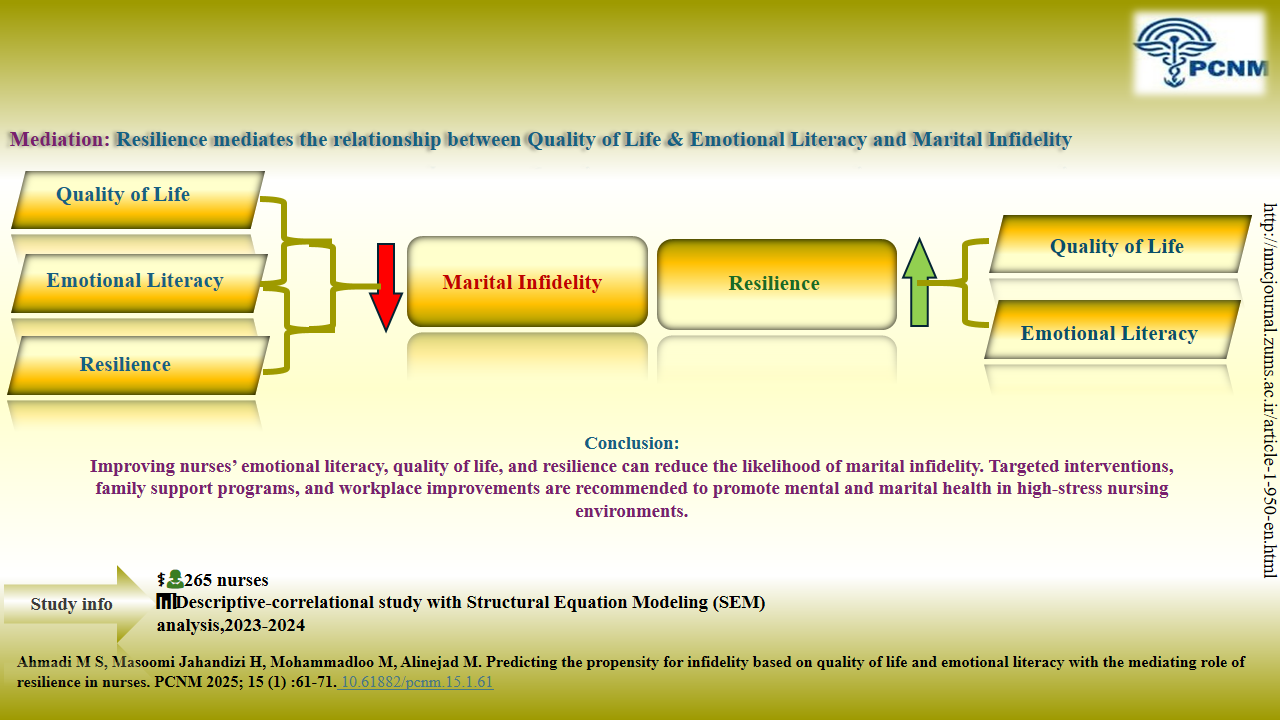
Results: The results revealed that the propensity for infidelity had significant negative correlations with quality of life (r =−0.38, p < 0.01), emotional literacy (r = −0.43, p < 0.01), and resilience (r=−0.49, p < 0.01). Furthermore, quality of life (β = 0.41, p < 0.01) and emotional literacy (β = 0.39, p < 0.01) had significant positive effects on resilience. The mediating role of resilience in the relationship between quality of life and emotional literacy with the propensity for infidelity was also confirmed (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: Emotional literacy and quality of life are effective variables in predicting the propensity for infidelity in nurses. Therefore, strengthening these skills can be beneficial in counseling and preventative interventions to reduce the likelihood of marital infidelity within this population.
Objectives: The present study aimed to predict the propensity for infidelity based on quality of life and emotional literacy, with resilience serving as a mediating role in nurses.
Methods: This descriptive correlational study, based on structural equation modeling (SEM), was conducted on 265 nurses in 2023-2024. Participants were recruited using a convenience sampling method. Data were collected using the Scale of Marital Infidelity (Bashirpour et al.), the Medical Outcomes Study (MOS) 36-item, Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36) (Ware & Sherbourne), the Emotional Literacy Scale (Kimiyaee), and the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC). Data were analyzed using Pearson’s correlation in SPSS version 25 and SEM in LISREL version 8.8.
Results: The results revealed that the propensity for infidelity had significant negative correlations with quality of life (r =−0.38, p < 0.01), emotional literacy (r = −0.43, p < 0.01), and resilience (r=−0.49, p < 0.01). Furthermore, quality of life (β = 0.41, p < 0.01) and emotional literacy (β = 0.39, p < 0.01) had significant positive effects on resilience. The mediating role of resilience in the relationship between quality of life and emotional literacy with the propensity for infidelity was also confirmed (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: Emotional literacy and quality of life are effective variables in predicting the propensity for infidelity in nurses. Therefore, strengthening these skills can be beneficial in counseling and preventative interventions to reduce the likelihood of marital infidelity within this population.
Full-Text [PDF 810 kb]
(882 Downloads)
| | Full-Text (HTML) (66 Views)
Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Nurse managers, hospital counselors, and nursing policymakers.
Low quality of life and poor emotional literacy increase nurses' risk of infidelity, but resilience can mitigate this risk. Implement workplace programs that enhance emotional literacy, improve quality of life, and build resilience to reduce infidelity risk among nurses.

Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Nurse managers, hospital counselors, and nursing policymakers.
Low quality of life and poor emotional literacy increase nurses' risk of infidelity, but resilience can mitigate this risk. Implement workplace programs that enhance emotional literacy, improve quality of life, and build resilience to reduce infidelity risk among nurses.
Type of Study: Orginal research |
Subject:
Nursing
References
1. 1. Cheraghi R, Almasi L, Alinejad V, Aghakhani N, Jasemi M, Eghtedar S. The relationship between emotional intelligence with job performance and occupational stress in nurses working in educational and medical centers in Urmia. Nursing And Midwifery Journal. 2023;21(7):575-588. [https://doi.org/10.61186/unmf.21.7.575]
2. Jor A, Sadeghmoghadam L, Mazloum Shahri SB, Khosravan S. The effect of a family-centered program to manage domestic roles on marital satisfaction in female nurses. Journal Of Research & Health. 2023;13(1):51-58. [https://doi.org/10.32598/JRH.13.1.2063.2]
3. Hackathorn J, Ashdown BK. The webs we weave: predicting infidelity motivations and extradyadic relationship satisfaction. Journal Of Sex Research. 2021;58:170-182. [https://doi.org/10.1080/00224499.2020.1746954] [PMID]
4. Gordon K, Mitchell EA. Infidelity in the time of COVID-19. Family Process. 2020;59(3):956-966. [https://doi.org/10.1111/famp.12576] [PMID]
5. Guerrero S, et al. Incidence and related factors of infidelity among medical doctors and nurses. International Journal Of Environmental Research And Public Health. 2021;18(11):5575. [https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115575] [PMID]
6. Afsharzada MS, Etemadi O, Naghavi A. Marital infidelity: cognitive, behavioral, emotional reactions, and coping strategies among Afghan women. Journal Of Research In Cognitive And Behavioral Sciences. 2025;14(2):13-26. [https://doi.org/10.22108/cbs.2024.141390.1901]
7. Adam A. Perceptions of infidelity: a comparison of sexual, emotional, cyber-, and parasocial behaviors. Interpersona: An International Journal On Personal Relationships. 2019;13(2):237-252. [https://doi.org/10.5964/ijpr.v13i2.376]
8. Ejeh PC. A philosophical examination of the concept and nature of infidelity in marriage as a socio-ethical issue in contemporary society. Social Sciences And Humanity Research. 2022;5(7):36-42. [https://zenodo.org/records/6907107]
9. Azhar A, et al. Linking infidelity stress, anxiety and depression: Evidence from Pakistan married couples and divorced individuals. International Journal Of Human Rights In Healthcare. 2018;11(3):214-228. [https://doi.org/10.1108/IJHRH-11-2017-0069]
10. Alexopoulos C, Taylor LD. Your cheating cognitions: young women's responses to television messages about infidelity. Mass Communication & Society. 2020;23(2):249-271. [https://doi.org/10.1080/15205436.2019.1705350]
11. WHOQOL Group. Measuring quality of life: the development of the World Health Organization Quality of Life Instrument (WHOQOL). Geneva: World Health Organization; 1992.
12. Byramvand Y, Omidi Arjenaki S, Salehzadeh. Prediction of tendency toward marital infidelity based on internet pornography use: the mediating role of marital relationship quality. Journal Of Applied Psychological Research. 2024;14(4):185-201. [https://doi.org/10.22059/japr.2024.336861.644159]
13. Ferdosi S. The prediction of attitudes toward infidelity based on attachment behavior in couple relationships, marital quality relationship and attachment styles in married women. Contemporary Psychology. 2018;13(2):149-157. [https://doi.org/10.29252/bjcp.13.2.149]
14. Zahiri A, Abbas B, Zabihullah S, AndA. The effectiveness of couple therapy based on improving the quality of life on conflict resolution styles, marital satisfaction and quality of life of couples with a history of breaking the contract. Family Psychology. 2019;2(7):1-16. [https://doi.org/10.22034/ijfp.2021.245573]
15. Urganci B, Sevi B, Sakman E. Better relationships shut the wandering eye: Sociosexual orientation mediates the association between relationship quality and infidelity intentions. Journal Of Social And Personal Relationships. 2021;38(4):1401-1409. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0265407521995261]
16. Shalchianpourkhaljan N, Asadi J, Hasanzadeh R, Khajvand Khoshly. The mediating role of cognitive emotion regulation in the relationship between attachment styles and emotional intelligence with tendency toward extramarital relationships. Taraqi-Ye Counseling & Psychotherapy Quarterly. 2022;11(43):26-38.
17. Teoli D, Bhardwaj A. Quality of Life in StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536962/]
18. Shaghaghi F, Agha Yousefi A, Mirza Hosseini H. Developing a structural model of the quality of the main family and the tendency to infidelity between spouses through the mediation of self-differentiation. Journal Of Psychological Science. 2021;20(108):2327-2342. [https://doi.org/10.52547/JPS.20.108.2327]
19. Swets JA, Cox CR. Insecure attachment and lower preference for romantic relationship nostalgia predict higher acceptance of infidelity. Personality And Individual Differences. 2023;203:112046. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2022.112006]
20. Shafiee Sabet M, Vahedi S, Bahramnezhad F, Dehghan Nayeri N. Investigating the relationship between presentism and resilience of critical care nurses of hospitals affiliated with Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Journal Of The Iranian Institute For Health Sciences Research (Payesh). 2023;22(6):727-735. [https://doi.org/10.61186/payesh.22.6.727]
21. Moshtaghi M, Asghari Ebrahimabad MJ, Salayani F. Associations between resilience and quality of life in nurses: the mediating role of emotional expressivity. Journal Of Mazandaran University Of Medical Sciences. 2020;30(191):53-65. [https://sid.ir/paper/963774/en]
22. Heydarian M, Eisanijad O. The effectiveness of quality of life-based therapy on functioning and quality of life of the families of freed prisoners of war. Military Psychology. 2020;11(44):45-59. [https://jmp.ihu.ac.ir/article_206025.html]
23. ALagheband L, Sharifi HP, Farzad V, Saghayousefi A. Predicting emotional divorce based on emotional literacy, coping styles, quality of life, and resilience mediation. Journal Of Psychological Science. 2020;19(90):733-743. [https://psychologicalscience.ir/article-1-603-fa.pdf]
24. Girma Shifaw Z. Marital communication as a moderator of the relationship between marital conflict resolution and marital satisfaction. American Journal Of Family Therapy. 2022;50(1):23-37.
25. Moor K, et al. Exploring how family carers of a person with dementia manage pre-death grief: A mixed methods study. International Journal Of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2023;38(3):586-597. [https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.5867] [PMID]
26. Kayode AD, Ogwunwuyi BO, Olaiya SF, Araromi CO. Emotional intelligence and marital satisfaction of Christian couples in CAC, Nigeria. Applied Journal Of Economics, Management, And Social Sciences. 2022;3(3):10-16. [https://doi.org/10.53790/ajmss.v3i3.59]
27. Kline RB. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. 4th ed. New York: Guilford Press; 2016.
28. Bashirpur M, Shafiabadi A, Dokaneheefard F. Psychometric properties of the scale of marital infidelity. Psychometric Quartely. 2018;6(24):37-55.
29. Asghari Moghadam MA, Faghihi S. Validity and reliability of the Health Survey Questionnaire (Short Form-36) in two Iranian samples. Clinical Psychology & Personality. 2003;1(1):1-10.
30. Veismoradi M, Borjali A, Rafezi Z. Predicting nurses' quality of life based on coronavirus-induced anxiety and cognitive flexibility. Bi-Quarterly Journal Of Clinical Psychology And Personality. 2023;21(1):171-180. [https://doi.org/10.22070/cpap.2023.16350.1237]
31. Kimiaee S, Khademian H, Farhadi H, Ghimati A. Develop and Study of Preliminary Psychometric and Validation Characteristic of Iranian Family Psychological Function Scale. Journal Of Modern Psychological Researches. 2012;7(27):145-182. [https://psychologyj.tabrizu.ac.ir/article_4124.html]
32. Connor KM, Davidson JR. Development of a new resilience scale: the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC). Depression And Anxiety. 2003;18(2):76-82. [https://doi.org/10.1002/da.10113] [PMID]
33. Sharif Nia H, She L, Froelicher ES, Marôco J, Moshtagh M, Hejazi S. Psychometric evaluation of the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale among the Iranian population. BMC Psychiatry. 2023;23(1):92. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-023-04580-8] [PMID]
34. Alameddine M, Bou-Karroum K, Ghalayini W, Abiad F. Resilience of nurses at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic in Lebanon. International Journal Of Nursing Sciences. 2021;8(4):432-438. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2021.08.002] [PMID]
35. Razmpush M, Ramezani K, Maredpour A, Koulivand PH. The role of self-efficacy and resilience in nurses' quality of life. Shefaye Khatam. 2019;7(1):34-42. [https://doi.org/10.29252/shefa.7.1.34]
36. Moshtaghqi M, Asghari Ebrahimabad M, Salayani F. The relationship between resilience and quality of life in nurses: the mediating role of emotional expressiveness. Journal Of Mazandaran University Of Medical Sciences. 2020;30(191):53-65. [https://www.sid.ir/paper/963774/fa]
37. Hu T, Zhang D, Wang J. A meta-analysis of the trait resilience and mental health. Personality And Individual Differences. 2015;76:18-27. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2014.11.039]
38. Zahednezhad H, Zareiyan A, Zargar Balaye Jame S. Relationship between quality of work-life, resilience and burnout among nursing professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic in Iran: a cross-sectional study. Belitung Nursing Journal. 2021;7(6):508-515. [https://doi.org/10.33546/bnj.1702] [PMID]
39. Tamrchi F, Asadpour I, Zahrakar K. Presenting a paradigmatic model of underlying factors resulting in marital infidelity based on grounded theory. Journal Of Psychological Science. 2021;20(107):2027-2043. [https://doi.org/10.52547/JPS.20.107.2027]
40. Najafizadeh M, Hamzehpoor-Haghighi T. The role of resilience, conflict resolution strategies, and sensation seeking in predicting attitude to marital infidelity of married female students of Lahijan Azad University. Community Health. 2022;9(1):15-24. [https://sid.ir/paper/1008962/en]
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |




