
Preventive Care in Nursing and Midwifery Journal

Volume 15, Issue 2 (10-2025)
Editorial
P. 1-2
Original Article
P. 3-12
Abstract
(657 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(185 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(138 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights


Knowlege Translation Statement
Audience: Nurses, midwives, rehabilitation specialists, and psychologists in disability care.
A structured mindful compassion program significantly reduces pain catastrophizing and rumination in women with mobility disabilities. Clinicians should integrate this intervention as a psychological adjunct to standard rehabilitation. Offering 8–12 weekly sessions focusing on self-kindness and mindful awareness can improve emotional regulation and pain-related coping. Routine screening for catastrophizing and rumination is recommended to identify suitable candidates.
Audience: Nurses, midwives, rehabilitation specialists, and psychologists in disability care.
A structured mindful compassion program significantly reduces pain catastrophizing and rumination in women with mobility disabilities. Clinicians should integrate this intervention as a psychological adjunct to standard rehabilitation. Offering 8–12 weekly sessions focusing on self-kindness and mindful awareness can improve emotional regulation and pain-related coping. Routine screening for catastrophizing and rumination is recommended to identify suitable candidates.
Original Article
P. 13-22
Mahtab Aligholipour 

 , Farhad Ramezani-Badr *
, Farhad Ramezani-Badr * 

 , Nasrin Hanifi
, Nasrin Hanifi 

 , Zahra Hormati Oghol Beig
, Zahra Hormati Oghol Beig 

 , Zahra Khezerlou
, Zahra Khezerlou 




 , Farhad Ramezani-Badr *
, Farhad Ramezani-Badr * 

 , Nasrin Hanifi
, Nasrin Hanifi 

 , Zahra Hormati Oghol Beig
, Zahra Hormati Oghol Beig 

 , Zahra Khezerlou
, Zahra Khezerlou 


Abstract
(449 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(149 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(148 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights
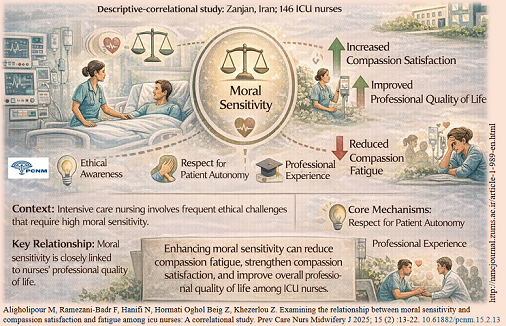

Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Nurse managers, hospital administrators, ethics educators, and clinical supervisors in critical care settings.
Higher moral sensitivity in ICU nurses is significantly linked to greater compassion satisfaction and lower compassion fatigue. To leverage this, healthcare institutions should implement mandatory, continuous ethics training programs focusing on respect for patient autonomy, professional knowledge, and ethical decision-making. Additionally, creating supportive work environments and establishing peer support groups are recommended preventive strategies to reduce burnout and enhance nurses' professional quality of life.
Audience: Nurse managers, hospital administrators, ethics educators, and clinical supervisors in critical care settings.
Higher moral sensitivity in ICU nurses is significantly linked to greater compassion satisfaction and lower compassion fatigue. To leverage this, healthcare institutions should implement mandatory, continuous ethics training programs focusing on respect for patient autonomy, professional knowledge, and ethical decision-making. Additionally, creating supportive work environments and establishing peer support groups are recommended preventive strategies to reduce burnout and enhance nurses' professional quality of life.
Original Article
P. 23-31
Abstract
(407 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(180 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(166 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights


Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Hospital administrators, nursing managers, healthcare policymakers, and nurse educators
Research shows that higher levels of burnout in nurses are directly linked to lower quality of caring behaviors. To protect care quality, healthcare organizations should implement structured workload management to prevent excessive demands and introduce mandatory emotional resilience and peer support training programs for nursing staff.
Audience: Hospital administrators, nursing managers, healthcare policymakers, and nurse educators
Research shows that higher levels of burnout in nurses are directly linked to lower quality of caring behaviors. To protect care quality, healthcare organizations should implement structured workload management to prevent excessive demands and introduce mandatory emotional resilience and peer support training programs for nursing staff.
Original Article
P. 32-41
Abstract
(336 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(126 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(81 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights


Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Mental health clinicians, primary care nurses, and counselors working with women at risk
Dysfunctional defense mechanisms in women increase suicidal ideation both directly and through the mediating effects of psychological pain and emotion regulation difficulties. Integrate screening for these factors into routine mental health assessments and prioritize interventions like emotion regulation training and psychological pain management to mitigate suicide risk.
Audience: Mental health clinicians, primary care nurses, and counselors working with women at risk
Dysfunctional defense mechanisms in women increase suicidal ideation both directly and through the mediating effects of psychological pain and emotion regulation difficulties. Integrate screening for these factors into routine mental health assessments and prioritize interventions like emotion regulation training and psychological pain management to mitigate suicide risk.
Original Article
P. 42-49
Abstract
(352 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(189 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(135 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights


Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Midwives, primary care nurses, and women's health educators
Inhalation aromatherapy with neroli oil (Citrus aurantium) significantly reduces pain intensity in primary dysmenorrhea more effectively than placebo. Integrate this safe, non-pharmacological intervention into routine care for menstrual pain management to reduce reliance on analgesics and improve quality of life.
Audience: Midwives, primary care nurses, and women's health educators
Inhalation aromatherapy with neroli oil (Citrus aurantium) significantly reduces pain intensity in primary dysmenorrhea more effectively than placebo. Integrate this safe, non-pharmacological intervention into routine care for menstrual pain management to reduce reliance on analgesics and improve quality of life.
Original Article
P. 50-58
Abstract
(621 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(212 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(202 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights


Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Midwives, public health nurses, clinic managers, and health policymakers
Women report moderate-to-low satisfaction with preconception and childbearing counseling, primarily due to insufficient education, poor communication, and structural barriers like privacy and accessibility. To improve care quality and align with fertility-promoting policies, services should adopt a family-centered approach, enhance provider communication skills, develop clear educational materials, and ensure confidential, respectful consultations.
Audience: Midwives, public health nurses, clinic managers, and health policymakers
Women report moderate-to-low satisfaction with preconception and childbearing counseling, primarily due to insufficient education, poor communication, and structural barriers like privacy and accessibility. To improve care quality and align with fertility-promoting policies, services should adopt a family-centered approach, enhance provider communication skills, develop clear educational materials, and ensure confidential, respectful consultations.
Original Article
P. 59-71
Abstract
(513 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(144 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(152 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights

Healthcare providers experienced the COVID-19 pandemic as a three-phase shock (alarm, struggle, exhaustion) but also as an empowering challenge that revealed systemic gaps and promoted integration, prevention, and public health awareness. To build resilient health systems, managers and policymakers must proactively stockpile supplies, invest in workforce training and telehealth infrastructure, and develop clear, adaptable crisis communication and management plans for future emergencies.

Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Health system managers, hospital administrators, policymakers, and public health professionalsHealthcare providers experienced the COVID-19 pandemic as a three-phase shock (alarm, struggle, exhaustion) but also as an empowering challenge that revealed systemic gaps and promoted integration, prevention, and public health awareness. To build resilient health systems, managers and policymakers must proactively stockpile supplies, invest in workforce training and telehealth infrastructure, and develop clear, adaptable crisis communication and management plans for future emergencies.
Review Article
P. 72-83
Abstract
(495 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(189 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(145 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights


Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Midwives, obstetric nurses, clinical researchers, and complementary therapy educators
Current high-quality evidence does not demonstrate a statistically significant effect of topical curcumin on episiotomy wound healing compared to standard care. Clinicians and educators should prioritize evidence-based standard perineal care and inform patients that the therapeutic benefit of curcumin for this specific use is not yet established. This review highlights a critical gap in the literature, underscoring the urgent need for larger, high-quality randomized controlled trials to definitively evaluate curcumin's efficacy and safety for postpartum perineal healing.
Audience: Midwives, obstetric nurses, clinical researchers, and complementary therapy educators
Current high-quality evidence does not demonstrate a statistically significant effect of topical curcumin on episiotomy wound healing compared to standard care. Clinicians and educators should prioritize evidence-based standard perineal care and inform patients that the therapeutic benefit of curcumin for this specific use is not yet established. This review highlights a critical gap in the literature, underscoring the urgent need for larger, high-quality randomized controlled trials to definitively evaluate curcumin's efficacy and safety for postpartum perineal healing.

