
Preventive Care in Nursing and Midwifery Journal

Volume 15, Issue 1 (1-2025)
PCNM 2025, 15(1): 1-9 |
Back to browse issues page
Ethics code: IR.ZUMS.REC.1397.367
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Hatef F, Gheiasi S F, Amini K. Communication skills of head nurses and its relationship to work engagement and psychological distress of staff nurses in the Iranian context: An observational multicenter study. PCNM 2025; 15 (1) :1-9
URL: http://nmcjournal.zums.ac.ir/article-1-932-en.html
URL: http://nmcjournal.zums.ac.ir/article-1-932-en.html
Department of Psychiatric Nursing, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjn, Iran , korosh@zums.ac.ir
Abstract: (1313 Views)
Background: The communication skills of head nurses with staff nurses are critical to supporting the job functions and effectiveness of a staff nurse, which directly impacts quality patient care.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the communication skills of head nurses and its relationship to work engagement and psychological distress of nurses.
Methods: This cross-sectional study conducted on 264 nurses. Participants were included in the study using Stratified randomization. Data were collected using a demographic information form, the MayfIeid's Motivational Language Scale, the Schaufelis Work Engagement Scale, and the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale.
Results: The mean (SD) score of head nurses' communication skills is [66.92 (20.69) out of 120]. Work engagement scores were [30.17 (12.04) out of 54] and psychological distress of nurses in the moderate levels [25.15 (8.77) out of 50], respectively. The relationship between head nurse's communication skills with work engagement of nurses was positive (r=0.34, p<0.001) and negative with nurses' psychological distress (r= -0.26, p<0.001). There was also a significant and inverse relationship between work engagement and nurses' psychological distress (r = -0.43, p< 0.001). Regression analysis showed that head nurses' communication skills predicted 11.7% of nurses' work engagement and 6.7% of nurses' psychological distress.
Conclusion: The communication skills of head nurses were moderate from the nurse's perspective. However, these skills are associated with high levels of nurses' work engagement and less psychological distress. Therefore, it is necessary to plan to implement programs to increase head nurses' communication skills and thus improve the quality of nursing care in the study population.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the communication skills of head nurses and its relationship to work engagement and psychological distress of nurses.
Methods: This cross-sectional study conducted on 264 nurses. Participants were included in the study using Stratified randomization. Data were collected using a demographic information form, the MayfIeid's Motivational Language Scale, the Schaufelis Work Engagement Scale, and the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale.
Results: The mean (SD) score of head nurses' communication skills is [66.92 (20.69) out of 120]. Work engagement scores were [30.17 (12.04) out of 54] and psychological distress of nurses in the moderate levels [25.15 (8.77) out of 50], respectively. The relationship between head nurse's communication skills with work engagement of nurses was positive (r=0.34, p<0.001) and negative with nurses' psychological distress (r= -0.26, p<0.001). There was also a significant and inverse relationship between work engagement and nurses' psychological distress (r = -0.43, p< 0.001). Regression analysis showed that head nurses' communication skills predicted 11.7% of nurses' work engagement and 6.7% of nurses' psychological distress.
Conclusion: The communication skills of head nurses were moderate from the nurse's perspective. However, these skills are associated with high levels of nurses' work engagement and less psychological distress. Therefore, it is necessary to plan to implement programs to increase head nurses' communication skills and thus improve the quality of nursing care in the study population.
Full-Text [PDF 886 kb]
(674 Downloads)
| | Full-Text (HTML) (42 Views)
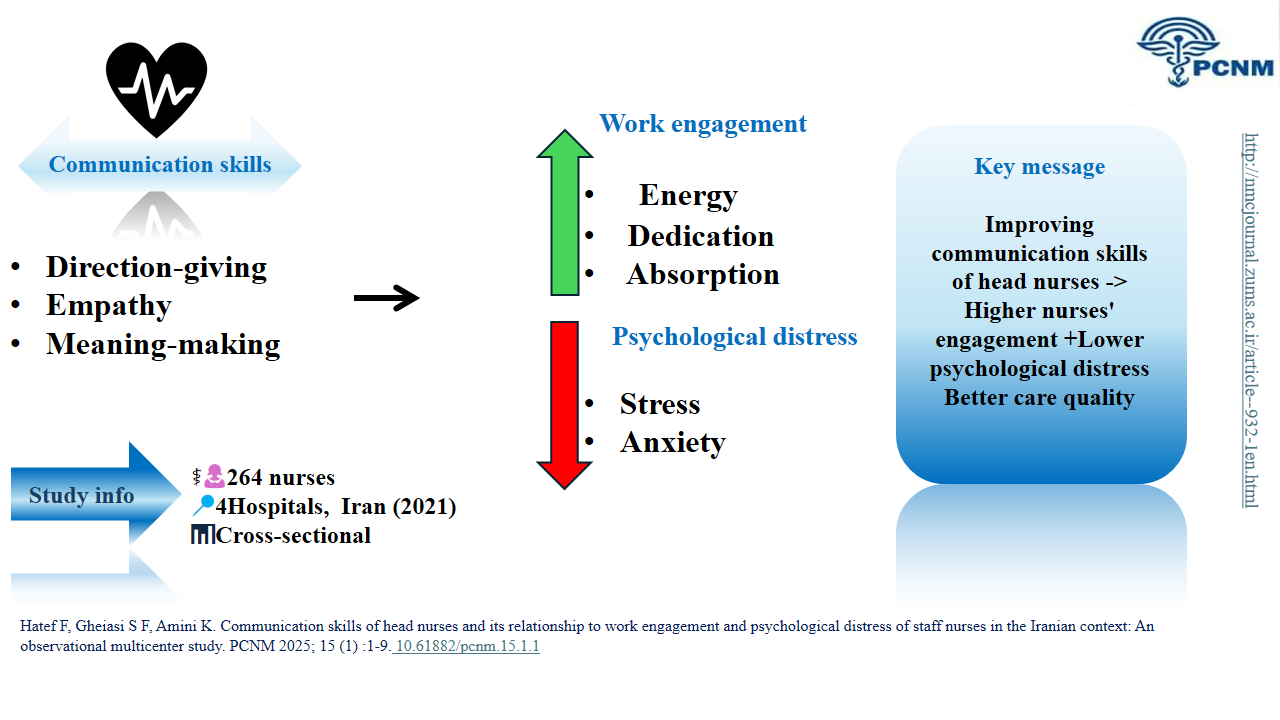
Knowlege Translation Statement
Audience: Nursing managers, hospital administrators, and health policy makers.
This study demonstrates that the communication skills of nurse managers, specifically in direction-giving, empathy, and meaning-making, are directly linked to higher work engagement and lower psychological distress among their nursing staff. Investing in targeted communication training for nursing leaders is therefore not merely a soft-skill initiative but a crucial strategy for enhancing workforce well-being and organizational performance in high-stress clinical environments.

Knowlege Translation Statement
Audience: Nursing managers, hospital administrators, and health policy makers.
This study demonstrates that the communication skills of nurse managers, specifically in direction-giving, empathy, and meaning-making, are directly linked to higher work engagement and lower psychological distress among their nursing staff. Investing in targeted communication training for nursing leaders is therefore not merely a soft-skill initiative but a crucial strategy for enhancing workforce well-being and organizational performance in high-stress clinical environments.
Type of Study: Orginal research |
Subject:
Nursing
Received: 2024/11/19 | Accepted: 2024/12/30 | Published: 2025/01/29
Received: 2024/11/19 | Accepted: 2024/12/30 | Published: 2025/01/29
References
1. Lewenson S. Public health nursing: Practicing population-based care. 2nd ed. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2017.
2. Saleh U, O'Connor T, Al-Subhi H, Alkattan R, Al-Harbi S, Patton D. The impact of nurse managers' leadership styles on ward staff. British Journal of Nursing. 2018;27(4):197-203. [https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2018.27.4.197] [PMID]
3. Balsanelli AP, David DR, Ferrari TG. Nursing leadership and its relationship with the hospital work environment. Acta Paulista de Enfermagem. 2018;31(2):187-93. [https://doi.org/10.1590/1982-0194201800027]
4. Perez-Gonzalez S, Marques-Sanchez P, Pinto-Carral A, Gonzalez-Garcia A, Liebana-Presa C, Benavides C. Characteristics of Leadership Competency in Nurse Managers: A Scoping Review. Journal of Nursing Management. 2024;2024:5594154. [https://doi.org/10.1155/2024/5594154] [PMID]
5. Nurmeksela A, Mikkonen S, Kinnunen J, Kvist T. Relationships between nurse managers' work activities, nurses' job satisfaction, patient satisfaction, and medication errors at the unit level: a correlational study. BMC Health Services Research. 2021;21:296. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-06288-5] [PMID]
6. Gunawan J, Aungsuroch Y, Fisher ML, Marzilli C, Hastuti E. Refining core competencies of first-line nurse managers in the hospital context: a qualitative study. International Journal of Nursing Sciences. 2023;10(4):492-500. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2023.08.001] [PMID]
7. Qtait M. Systematic Review of Head Nurse Leadership Style and Nurse Performance. International Journal of Africa Nursing Sciences. 2023;18:100564. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijans.2023.100564]
8. Mirzaei A, Imashi R, Saghezchi RY, Jafari MJ, Nemati-Vakilabad R. The relationship of perceived nurse manager competence with job satisfaction and turnover intention among clinical nurses: an analytical cross-sectional study. BMC Nursing. 2024;23:528. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-02203-5] [PMID]
9. Hadi-Moghaddam M, Karimollahi M, Aghamohammadi M. Nurses' trust in managers and its relationship with nurses' performance behaviors: a descriptive-correlational study. BMC Nursing. 2021;20:147. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-021-00653-9] [PMID]
10. Ghahremani L, Khoramaki Z, Kaveh MH, Karimi M, Nazari M, Orgambídez Ramos A. Communication Self‐Efficacy and Job Satisfaction among Nurses during the COVID‐19 Pandemic. Journal of Nursing Management. 2024;2024:8869949. [https://doi.org/10.1155/2024/8869949] [PMID]
11. Asefzadeh S, Mohammadi M. The relationship between Head-nurses' communication skills and demographic characteristics in educational hospoitals of sanandaj: A Cross Sectional study. Zanko Journal of Medical Sciences. 2018;18(59):48-56. [https://zanko.muk.ac.ir/article-1-212-en.html]
12. Wang CH, Anthony K, Kuo NW. The role of head nurse on communication: A social network approach. International Journal of Future Computer and Communication. 2016;5(1):43-6. [https://doi.org/10.18178/ijfcc.2016.5.1.441]
13. Kunie K, Kawakami N, Shimazu A, Yonekura Y, Miyamoto Y. The relationship between work engagement and psychological distress of hospital nurses and the perceived communication behaviors of their nurse managers: A cross-sectional survey. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2017;71:115-24. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2017.03.011] [PMID]
14. Schaufeli WB, Bakker AB, Salanova M. The measurement of work engagement with a short questionnaire: A cross-national study. Educational and Psychological Measurement. 2006;66(4):701-16. [https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164405282471]
15. Van Bogaert P, van Heusden D, Timmermans O, Franck E. Nurse work engagement impacts job outcome and nurse-assessed quality of care: model testing with nurse practice environment and nurse work characteristics as predictors. Frontiers in Psychology. 2014;5:1261. [https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01261] [PMID]
16. Wei H, Horsley L, Cao Y, Haddad LM, Hall KC, Robinson R, et al. The associations among nurse work engagement, job satisfaction, quality of care, and intent to leave: A national survey in the United States. International Journal of Nursing Sciences. 2023;10(4):476-84. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2023.09.010] [PMID]
17. Okazaki E, Nishi D, Susukida R, Inoue A, Shimazu A, Tsutsumi A. Association between working hours, work engagement, and work productivity in employees: A cross-sectional study of the Japanese Study of Health, Occupation, and Psychosocial Factors Relates Equity. Journal of Occupational Health. 2019;61(2):182-8. [https://doi.org/10.1002/1348-9585.12023] [PMID]
18. Birgani A. The relationship of work Engagement and work stress with satisfaction from daily lives of nurses in Ahvaz governmental hospitals. Jentashapir Journal of Health Research. 2013;4(2):141-9. Available from: https://brief.land/jjhr/articles/81938.html [https://brief.land/jjhr/articles/81938.html]
19. Akharbin P, Zahed Babolan A, Naghizadeh Baghi A. The relationship between servant leadership & organizational learning and nurses' work engagement. Journal of Research Development in Nursing and Midwifery. 2014;11(1):91-8. [https://nmj.goums.ac.ir/article-1-549-en.html]
20. Ren Z, Zhao H, Zhang X, Li X, Shi H, He M, et al. Associations of job satisfaction and burnout with psychological distress among Chinese nurses. Current Psychology. 2023;42:29161-71. [https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-04006-w] [PMID]
21. Babapour AR, Gahassab-Mozaffari N, Fathnezhad-Kazemi A. Nurses' job stress and its impact on quality of life and caring behaviors: a cross-sectional study. BMC Nursing. 2022;21:75. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-022-00852-y] [PMID]
22. Salehi A, Javanbakht M, Ezzatababdi MR. Stress and its determinants in a sample of Iranian nurses. Holistic Nursing Practice. 2014;28(5):323-8. [https://doi.org/10.1097/HNP.0000000000000043] [PMID]
23. Mayfield J, Mayfield M, Kopf J. The effects of leader motivating language on subordinate performance and satisfaction. Human Resource Management. 1998;37(3‐4):235-48.
https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-050X(199823/24)37:3/4<235::AID-HRM6>3.0.CO;2-X [https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-050X(199823/24)37:3/43.0.CO;2-X]
24. Ghanbari S, Ardalan M, Zandi K, Saifpanahi H. Validity and Reliability of Utrecht Nine-item Work Engagement Scale (UWES-9). Management and Development Process. 2015;28(2):181-97. [https://jmdp.ir/article-1-1665-en.html]
25. Kessler RC, Barker PR, Colpe LJ, Epstein JF, Gfroerer JC, Hiripi E, et al. Screening for serious mental illness in the general population. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2003;60(2):184-9. [https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.60.2.184] [PMID]
26. Ataei J, Morteza-Shamshirgaran S, Iranparvar M, Safaeian A, Malek A. Reliability and validity of the Persian version of the Kessler psychological distress scale among patients with type 2 diabetes. Journal of Research in Clinical Medicine. 2015;3(2):99-106. [https://doi.org/10.15171/jarcm.2015.015]
27. Eghtedar S, Soheili A, Nemati S. The communication skills of nursing managers and their associations with nurses' job satisfaction and anxiety. Nursing and Midwifery Journal. 2023;21(9):708-17. [https://doi.org/10.61186/unmf.21.9.708]
28. Dehghan Nayeri N, Varvani Farahani A, Sharifi N, Hoseini M, Aghabarary M. Effects of a Staff Development Program on Head Nurses' Communication Skills and Job Satisfaction. Nursing and Midwifery Studies. 2012;1(2):62-6. [https://doi.org/10.5812/nms.8562]
29. Jenaro C, Flores N, Orgaz MB, Cruz M. Vigour and dedication in nursing professionals: towards a better understanding of work engagement. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2011;67(4):865-75. [https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2010.05526.x] [PMID]
30. Vaghar Seyyedin SA, M SM. Relationship between nurses' work engagement, structural empowerment, and workplace incivility. Quarterly Journal of Nursing Management. 2015;4(1):18-27. [https://ijnv.ir/article-1-251-en.html]
31. Mason VM, Leslie G, Clark K, Lyons P, Walke E, Butler C, et al. Compassion fatigue, moral distress, and work engagement in surgical intensive care unit trauma nurses: a pilot study. Dimensions of Critical Care Nursing. 2014;33(4):215-25. [https://doi.org/10.1097/DCC.0000000000000056] [PMID]
32. Akbari F, Amirabadizadeh H, Poor Reza A, Vagheie Y, Dastjerdi R. Survey of socio-psychological stresses among nurses working in Birjand teaching hospitals in 2004. Journal of Birjand University of Medical Sciences. 2005;12(3):9-15. [https://journal.bums.ac.ir/article-1-76-en.html]
33. Okwaraji F, En A. Burnout and psychological distress among nurses in a Nigerian tertiary health institution. African Health Sciences. 2014;14(1):237-45. [https://doi.org/10.4314/ahs.v14i1.37] [PMID]
34. Zou G, Shen X, Tian X, Liu C, Li G, Kong L, et al. Correlates of psychological distress, burnout, and resilience among Chinese female nurses. Industrial Health. 2016;54(5):389-95. [https://doi.org/10.2486/indhealth.2015-0103] [PMID]
35. Farhadi M, Hemmati Maslakpak M, Khalkhali H. Job stressors in critical care nurses. Nursing and Midwifery Journal. 2014;11(11):1-9. [https://unmf.umsu.ac.ir/article-1-1697-en.html]
36. Kanter RM. Power failure in management circuits. In: Pugh DS, editor. Leadership perspectives. Routledge; 2017. p. 281-90. [https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315250601-21]
37. Othman N, Nasurdin AM. Social support and work engagement: a study of Malaysian nurses. Journal of Nursing Management. 2013;21(8):1083-90. [https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2834.2012.01448.x] [PMID]
38. Li H, Shi Y, Li Y, Xing Z, Wang S, Ying J, et al. Relationship between nurse psychological empowerment and job satisfaction: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2018;74(6):1264-77. [https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.13549] [PMID]
39. Inoue A, Kawakami N, Tsuno K, Shimazu A, Tomioka K, Nakanishi M. Job demands, job resources, and work engagement of Japanese employees: a prospective cohort study. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health. 2013;86:441-9. [https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-012-0777-1] [PMID]
40. Mayfield J, Mayfield M. Motivating language theory: Effective leader talk in the workplace. Springer; 2017. [https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66930-4]
41. Akbari M, Seyyed Amiri N, Imani S, Rezaeei N, Foroudi P. Why leadership style matters: a closer look at transformational leadership and internal marketing. The Bottom Line. 2017;30(4):258-78. [https://doi.org/10.1108/BL-08-2017-0021]
42. Bakker AB, Schaufeli WB, Leiter MP, Taris TW. Work engagement: An emerging concept in occupational health psychology. Work & Stress. 2008;22(3):187-200. [https://doi.org/10.1080/02678370802393649]
43. Inoue A, Kawakami N, Ishizaki M, Shimazu A, Tsuchiya M, Tabata M, et al. Organizational justice, psychological distress, and work engagement in Japanese workers. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health. 2010;83:29-38. [https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-009-0485-7] [PMID]
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |




