
Preventive Care in Nursing and Midwifery Journal

Volume 15, Issue 1 (1-2025)
Editorial
P. 1-2
Original Article
P. 3-11
Abstract
(1769 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(855 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(249 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights
Knowlege Translation Statement
Audience: Nursing managers, hospital administrators, and health policy makers.
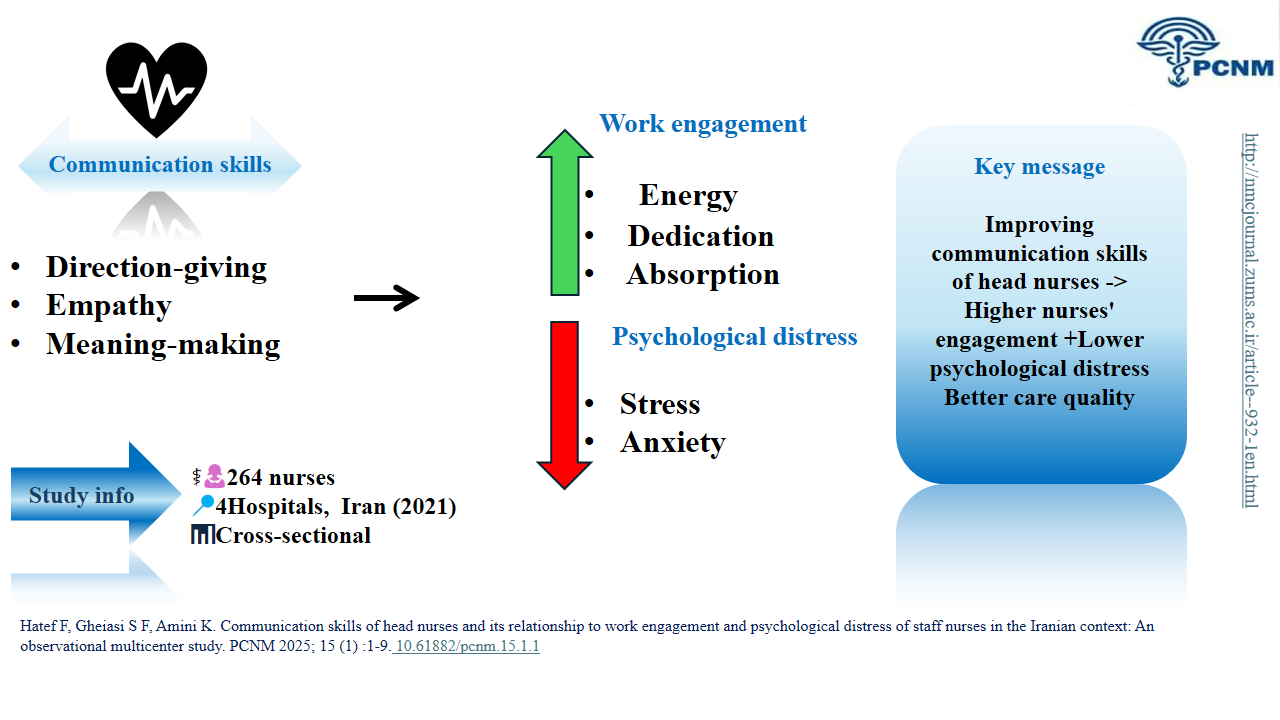
This study demonstrates that the communication skills of nurse managers, specifically in direction-giving, empathy, and meaning-making, are directly linked to higher work engagement and lower psychological distress among their nursing staff. Investing in targeted communication training for nursing leaders is therefore not merely a soft-skill initiative but a crucial strategy for enhancing workforce well-being and organizational performance in high-stress clinical environments.

Knowlege Translation Statement
Audience: Nursing managers, hospital administrators, and health policy makers.
This study demonstrates that the communication skills of nurse managers, specifically in direction-giving, empathy, and meaning-making, are directly linked to higher work engagement and lower psychological distress among their nursing staff. Investing in targeted communication training for nursing leaders is therefore not merely a soft-skill initiative but a crucial strategy for enhancing workforce well-being and organizational performance in high-stress clinical environments.
Original Article
P. 12-21
Abstract
(1351 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(831 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(123 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights


Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Nursing managers, midwives, and maternal health policymakers.
Domestic violence increases postpartum depression (PPD) risk both directly and by reducing marital satisfaction. Integrating routine screening for domestic violence and relationship quality into postpartum care is essential. Interventions supporting victims and improving marital satisfaction can significantly reduce PPD and enhance maternal and child health outcomes.
Original Article
P. 22-29
Abstract
(1131 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(530 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(114 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights

Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Nursing home managers, geriatric care planners, and health policymakers.
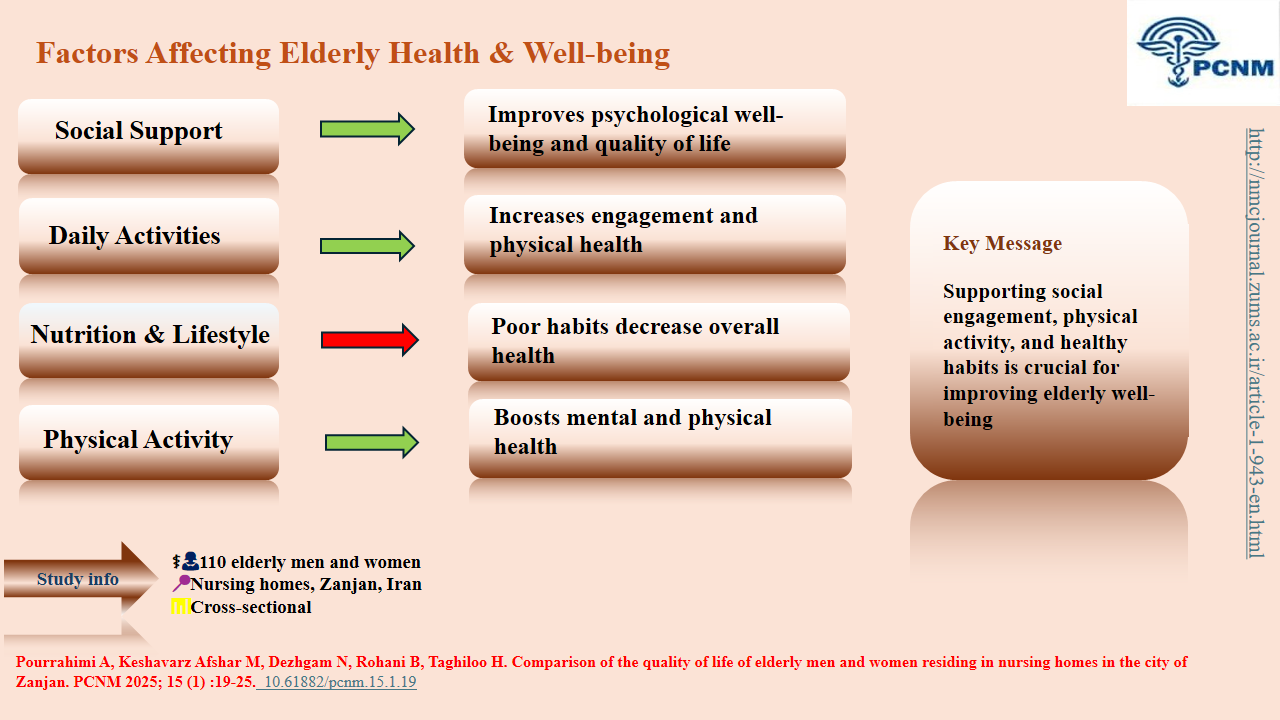
Elderly women in nursing homes experience a significantly lower quality of life than men, especially in physical and mental health. Care programs must be gender-sensitive, with targeted support for women's unique needs, to effectively improve well-being for all residents.Original Article
P. 30-36
Lintang Arum Nikentari 

 , Heri Kristianto *
, Heri Kristianto * 

 , Laily Yuliatun
, Laily Yuliatun 

 , Ali Haedar
, Ali Haedar 

 , Paulus Lucky Tirma Irawan
, Paulus Lucky Tirma Irawan 




 , Heri Kristianto *
, Heri Kristianto * 

 , Laily Yuliatun
, Laily Yuliatun 

 , Ali Haedar
, Ali Haedar 

 , Paulus Lucky Tirma Irawan
, Paulus Lucky Tirma Irawan 


Abstract
(1106 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(745 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(35 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights
Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Emergency Department managers, emergency nurses, and clinical policymakers.
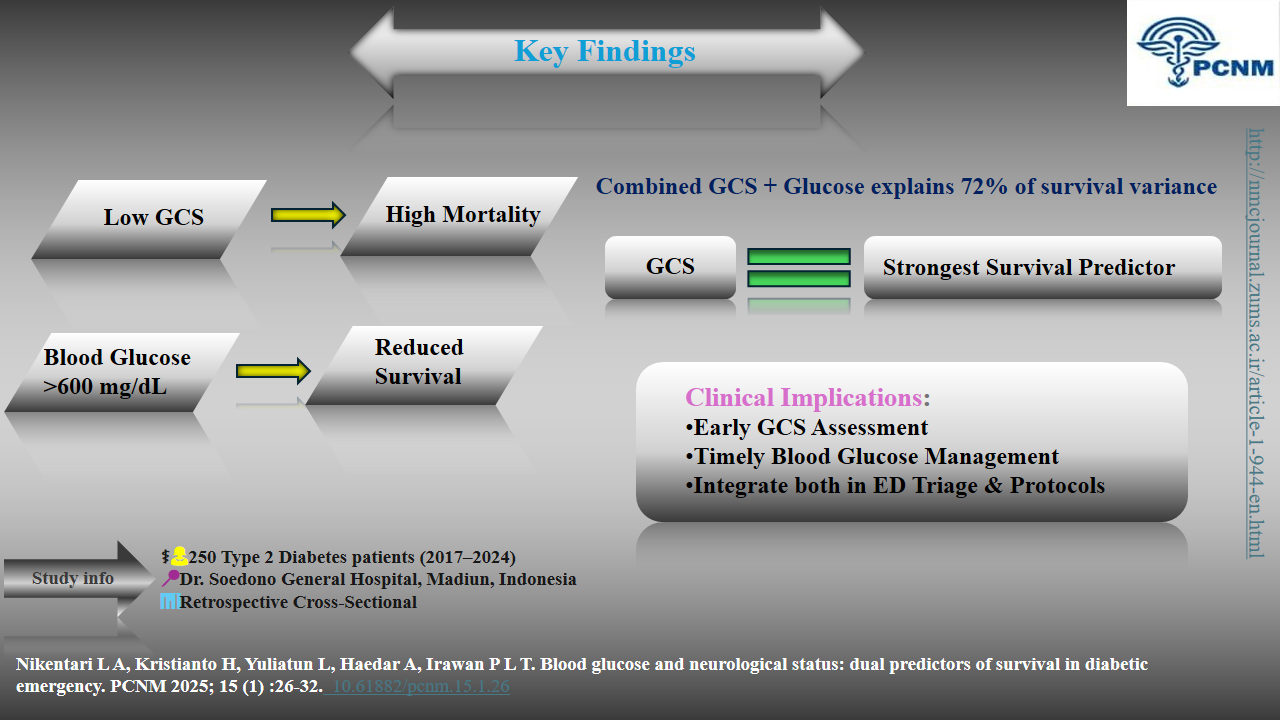
In diabetic emergencies, a low Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score is the strongest predictor of mortality, even more critical than extreme blood glucose levels. Triage protocols must prioritize immediate neurological assessment alongside glucose management to identify high-risk patients and guide life-saving interventions.

Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Emergency Department managers, emergency nurses, and clinical policymakers.
In diabetic emergencies, a low Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score is the strongest predictor of mortality, even more critical than extreme blood glucose levels. Triage protocols must prioritize immediate neurological assessment alongside glucose management to identify high-risk patients and guide life-saving interventions.
Original Article
P. 37-45
Abstract
(868 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(449 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(45 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights

Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: School nurses, adolescent psychologists, and public health educators.
Family functioning is a stronger predictor of reduced anxiety in adolescent girls than emotional expressiveness. Supportive family environments are crucial for prevention.
Routinely assess family dynamics in school mental health screenings and implement family-focused educational programs to build communication and problem-solving skills.

Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: School nurses, adolescent psychologists, and public health educators.
Family functioning is a stronger predictor of reduced anxiety in adolescent girls than emotional expressiveness. Supportive family environments are crucial for prevention.
Routinely assess family dynamics in school mental health screenings and implement family-focused educational programs to build communication and problem-solving skills.
Original Article
P. 46-55
Abstract
(751 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(314 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(8 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights
Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: First aid instructors, emergency training coordinators, and volunteer organization managers.
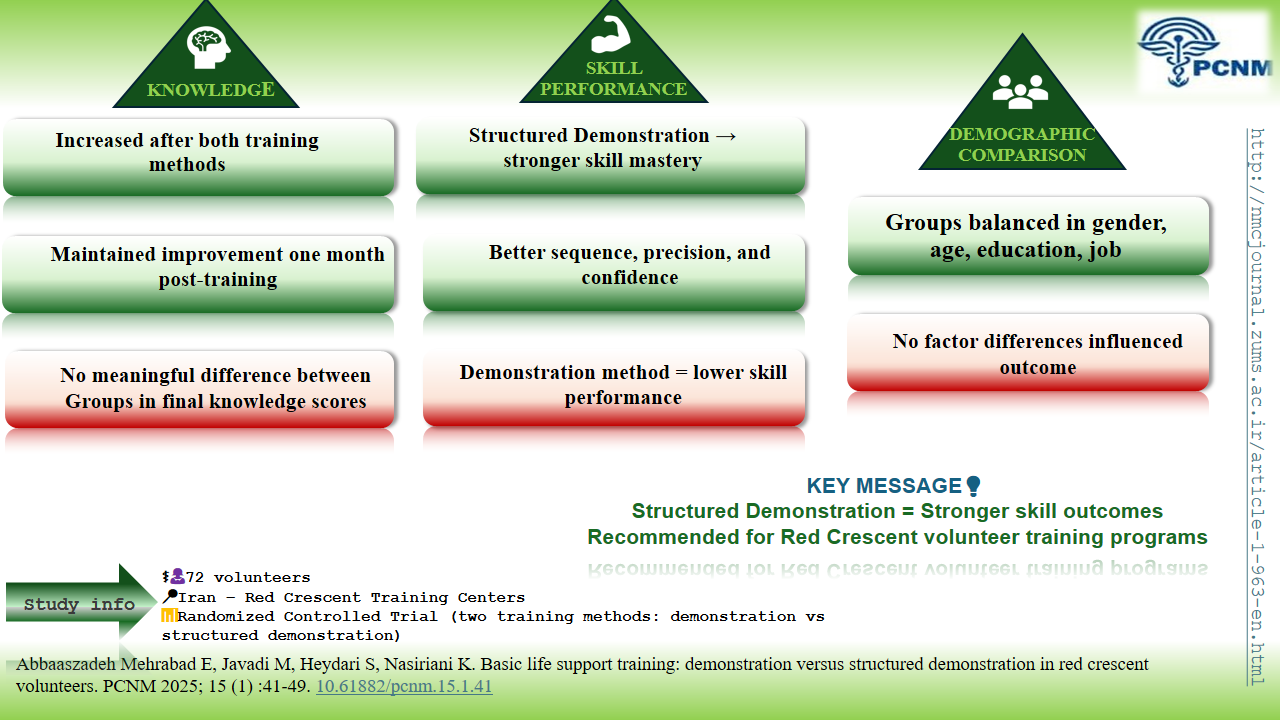
Structured demonstration training is superior to simple demonstration for developing practical CPR skills in volunteers, leading to significantly higher skill retention.
Implement structured demonstration in first aid programs, as its systematic approach (silent demo, commentary, and group practice) ensures better skill acquisition for lay responders.

Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: First aid instructors, emergency training coordinators, and volunteer organization managers.
Structured demonstration training is superior to simple demonstration for developing practical CPR skills in volunteers, leading to significantly higher skill retention.
Implement structured demonstration in first aid programs, as its systematic approach (silent demo, commentary, and group practice) ensures better skill acquisition for lay responders.
Original Article
P. 56-66
Abstract
(381 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(237 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(43 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights
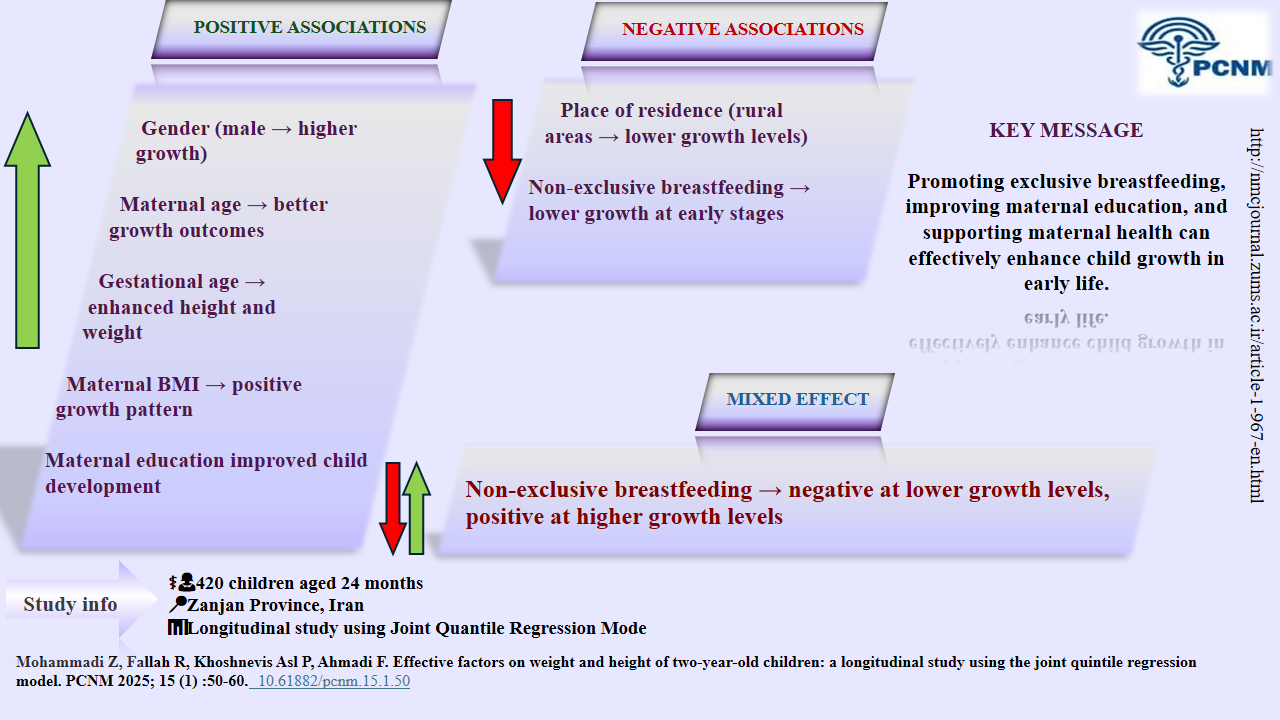

Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Pediatric nurses and community health planners.
Maternal education, gestational age, and rural residence significantly impact child growth. Target rural and less-educated mothers with growth monitoring, breastfeeding support, and prenatal care education.
Audience: Pediatric nurses and community health planners.
Maternal education, gestational age, and rural residence significantly impact child growth. Target rural and less-educated mothers with growth monitoring, breastfeeding support, and prenatal care education.
Original Article
P. 67-76
Abstract
(803 Views) |
Full-Text (PDF)
(690 Downloads)
|
Full-Text (HTML)
(38 Views)
| Graphical Abstract
| Highlights
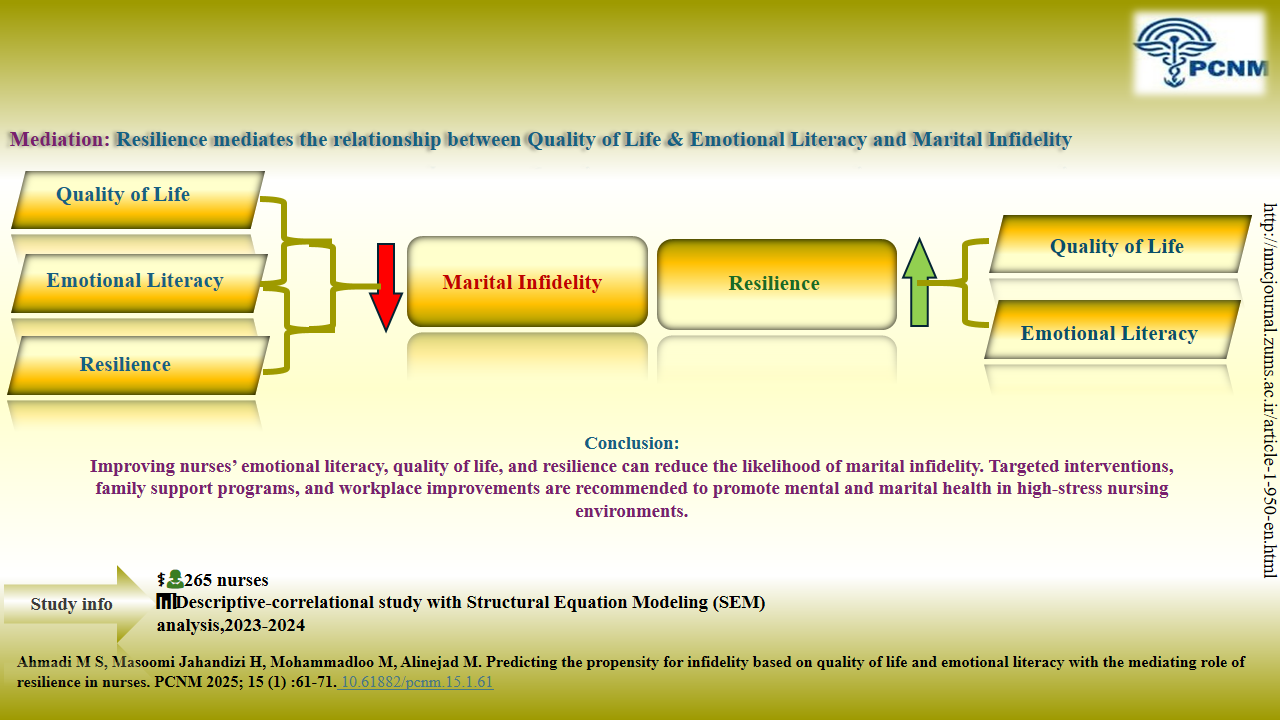
Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Nurse managers, hospital counselors, and nursing policymakers.
Low quality of life and poor emotional literacy increase nurses' risk of infidelity, but resilience can mitigate this risk. Implement workplace programs that enhance emotional literacy, improve quality of life, and build resilience to reduce infidelity risk among nurses.

Knowledge Translation Statement
Audience: Nurse managers, hospital counselors, and nursing policymakers.
Low quality of life and poor emotional literacy increase nurses' risk of infidelity, but resilience can mitigate this risk. Implement workplace programs that enhance emotional literacy, improve quality of life, and build resilience to reduce infidelity risk among nurses.

